Democracy
The basics
Agenda
- Conceptualizing Democracy
- Measuring Democracy
- Majoritarian Threat to Democracy (Grossman et. al.)
- On Wed: Democracy and development (And Fixed Effects)
What is Democracy?
Not an easy question to answer!
One might even say polemic…
Etymology? Demokratia = demos + kratia
Is it about elections? About outcomes? About norms?
Academics often talk about minimalist (procedural)
and maximalist (substantive) conceptions of democracy.
What is Democracy? The Minimalists
Democracy as a PROCEDURE for choosing and replacing who rules us
Schumpeter: a system in which rulers are selected by competitive elections
Popper: a system in which citizens can replace governments without bloodshed
Przeworksi: a system in which citizens collectively decide by whom and, to some extent, how they will be governed
What is Democracy? The Maximalists
“Thick’’ definition of democracy
Democracy as system that embodies or a method for realizing extrinsic values
Democracies classified based on formal institutions and rules, how those institutions are used in practice, and what outcomes they produce
- Do the rules, the way they are used, and their consequences promote equality, accountability, participation, justice, dignity, security …
Minimalists vs. Maximalists
Common critique of procedural conceptions of democracy:
is that it is too thin and mostly electoral.
But is it really that minimal?
- What do we require to hold “free and fair” elections?
- At least civil and political rights, neutral electoral machinery, stability, competing parties, etc…
- Respect for the rules of the game …
- What do we require to hold “free and fair” elections?
Minimalists vs. Maximalists
Common critique of maximalist perspective:
Democracy becomes subjective
- Whatever values we view as democratic need not be the other persons’ views
- Hard to measure, hard to compare across time and space
If democracy is only justifiable for its outcomes, we may risk autocracy during bad times
Are you a maximalist or a minimalist?
What is a necessary condition for a system to be democratic?
Does it need to hold elections?
Does everyone need to be able to vote?
Does everyone need to be able to run for office?
Have an independent legislative body?
Independent media?
Economic equality?
What is an autocracy
- A fundamentally residual category!
Measuring democracy
- Minimalist (Yes/No)
- Democracy-Dictatorship score (ends in 2008 sadly)
- Democracy if: Executive is elected, legislature is elected, more than one party, has been an alternation of power under current rules
- Democracy-Dictatorship score (ends in 2008 sadly)
- Maximalist
-
- Spectrum of: competitiveness, openness, participation, checks and balances
Freedom house (0-100)
- Experts rate: access to political rights and civil liberties
-
The Value of Democracy
Per se
- The fairest system as normatively desirable.
- Political freedom is human freedom.
Instrumental (i.e gets you something else)
The best way to prevent abuse is by making our rulers dependent on us.
We can select the most competent rulers.
Pacification of the political life.
Economic Development
If Democracy is Valuable…
Then we want to keep it safe!
Democracies are stronger when citizens hold politicians accountable
But… what if people knowingly support antidemocratic governments or antidemocratic behavior from politicians?
The Majoritarian Threat to Liberal Democracy
Grossman, Kronick, Levendusky, and Meredith, 2022
Puzzle: voters often ignore or even support politicians’ power grabs. Why?
Extant research shows some people prefer nondemocratic governments (autocrats)
While others prioritize their partisan objectives over democratic principals (militants)
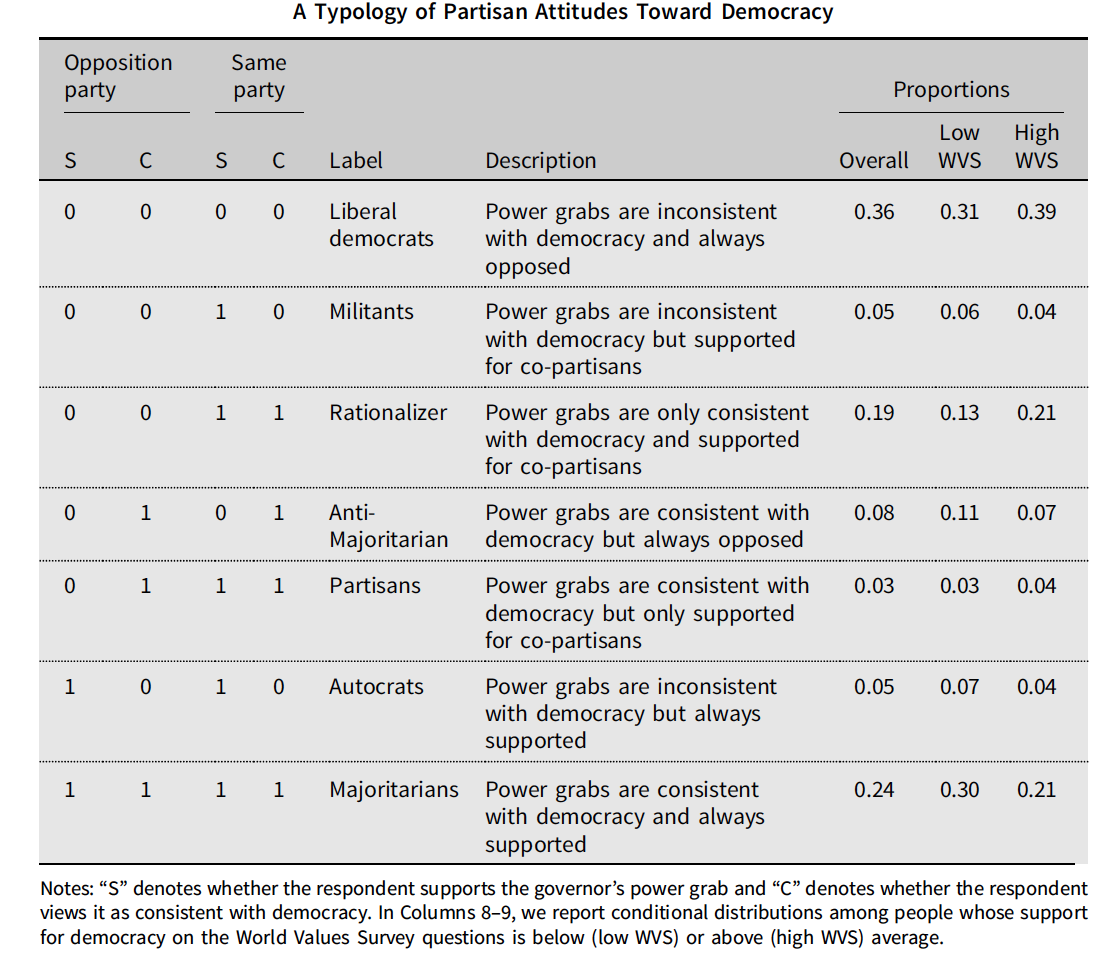
- But the authors suggest there is a third type …
The Majoritarian Threat to Liberal Democracy
- Majoritarians:
People who believe popular elected leaders are justified in taking legal but “antidemocratic” steps
What do we mean by that?
How to identify these people in the population?
Research Design
Two survey experiments. We will focus on the first one
Vignette –> outgoing governor announces that he will appoint a replacement for a state SCJ instead of waiting for incoming governor from opposite party
- Not illegal but not “democratic”
Respondents are assigned to a treatment or control condition.
What is the treatment?
Research Design
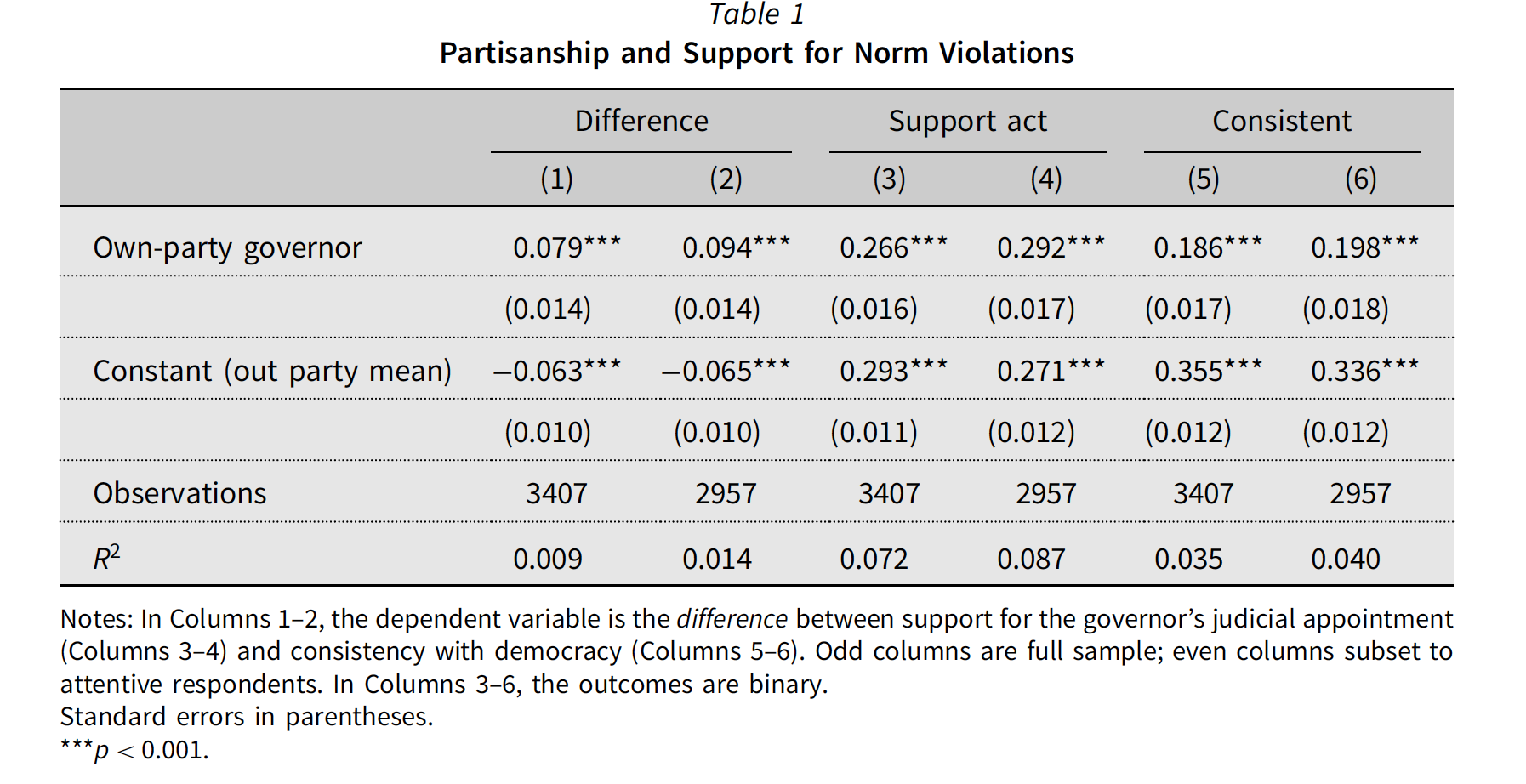
Randomly assigned whether the outgoing governor is a co-partisan of respondents
Outcomes?
- Do you approve of what the outgoing governor did?
- Do you think it’s consistent with democracy?
Assumptions?
- Treatment and control groups are the same across all relevant dimensions, in expectation
Theoretical Expectations
Results
Discussion
Are majoritarians antidemocratic? Are partisans?
- What would the minimalists say?
- What would the maximalists say?
What implications does the existence of majoritarians have for democratic quality?