Autocratization and Survey Experiments
Logistics
Assignments
- Today
- 3 readings
- Ensure Quarto is installed
- Thursday
- Create a git repo for this class (psci3200_yourname)
- DSS Ch4
Agenda
- Finishing up Final Project
- RStudio and Quarto
- Survey Experiments
- Overview
- Albertus & Grossman
- Hollerbauer et al.
Final Project
Examples of research questions
- Do citizens with mobile internet access have more negative opinions about their government?
- Do citizens that migrate have more or less positive views about democracy?
- Are domestic media outlets less likely to report on political events after elections?
RStudio and Quarto
Poll
- Mac vs Windows vs Other?
- Quarto running?
Instructions
- Follow-along as I create a quarto page
- Submit the html for the page to me via Slack before the end of class
Survey Experiments
What are survey experiments?
Two general uses
- Measuring sensitive attitudes
- Providing anonymity
- Identifying causal effect
- Manipulating images and text
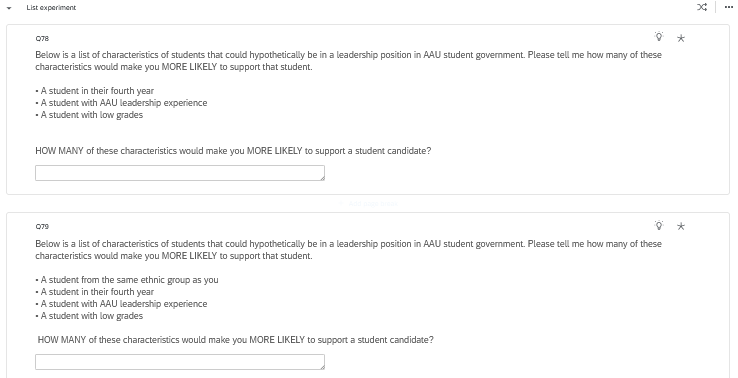
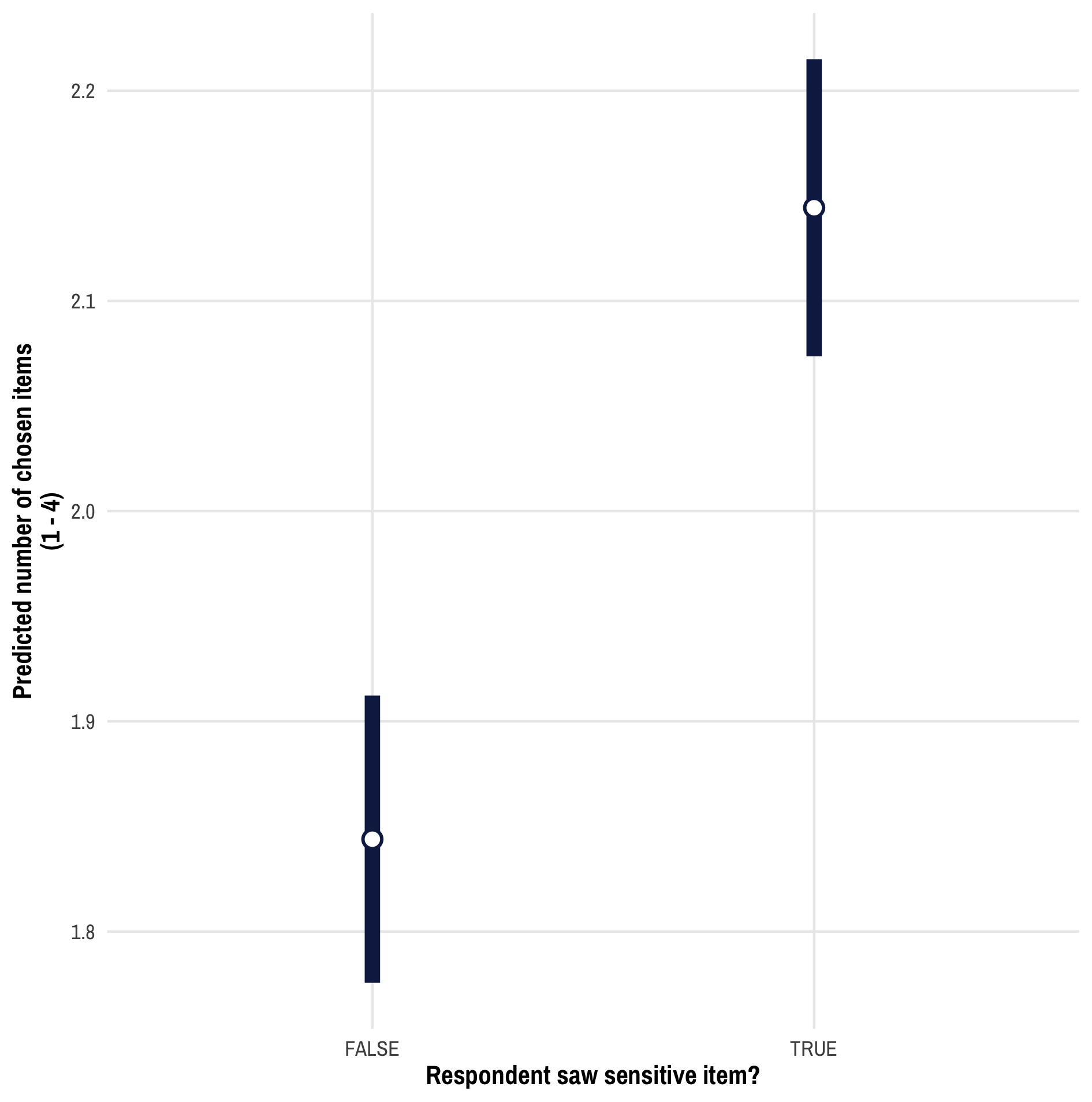
List Experiments
- What can list experiments tell us?
- prevalence of the sensitive attitude in the survey population
- What can they not tell us
- attitude of any individual respondent
- When might this be useful?
- Assessing prevalence of something
- Quantifying measurement bias/misreporting
List Experiments
Randomized Response
- What is it?
- Induce some \(p > 0\) that you say “Yes” even if you disagree
- Pitfalls
- Complexity, confusion
- Lack of anonymity
- Variants
- Repeated randomized response
- Crosswise
Priming
- What is it?
- Measures implicit attitudes by stimulating unconscious association
- Pitfalls
- Hard to know if the prime worked (false negative, confounding, etc.)
Confounding: Any experimental intervention A that is meant to trigger mental construct M could also trigger mental construct C. If C is not varied in the experimental design, researchers cannot determine whether M, C, or a combination of M and C affect outcomes of interest.
Vignettes and Factorials
- What is it?
- Presents a scenario while varying key components
- Pitfalls
- Unrealistic combinations
- Limited power
Conjoints
- What is it?
- Presents pair of profiles while varying attributes
- Asks respondents to choose between profiles
- Pitfalls
- Requires careful attention
- Can be highly synthetic
Albertus & Grossman
Background
Decline in the quantity and quality of democracies
- Executive power grabs rather than coups
- Weaken judiciary and media independence
- Purge bureaucracy and neutralize legislature
- Reduce political competition through legal changes
Research Questions
- Why do many voters support or ignore antidemocratic actions?
- Why are transgressions rarely punished?
- How is public opinion affected by means and justification?
Research Question
Why don’t citizens resist?
- Citizens don’t realize
- Should identify and oppose
- Citizens are conditional democrats (trade-off w/ideology)
- Should identify and support conditional on ideology
- Citizens may have differing conceptions of democracy
- Don’t identify as antidemocratic
What’s the Research Design?
Vignette Experiment
- Manipulation
- Antidemocratic behavior
- Partisan alignment
- Means and justifications
- Outcomes
- Perceived as antidemocratic
- Support for action
- Support for punishment
Findings
- Positive
- Respondents identify antidemocratic actions and oppose them
- Means and justifications do not increase support
- Negative
- Significant minority supports antidemocratic actions
- Partisan power increases support
Editorial Notes
Pushes back against polarization based explanations, which predict that people support antidemocratic behaviors because they view the other side as so dangerous
Policy Implications?
- Normalize punishment
- Emphasize long-run risks