Attaching package: 'ggdag'The following object is masked from 'package:stats':
filter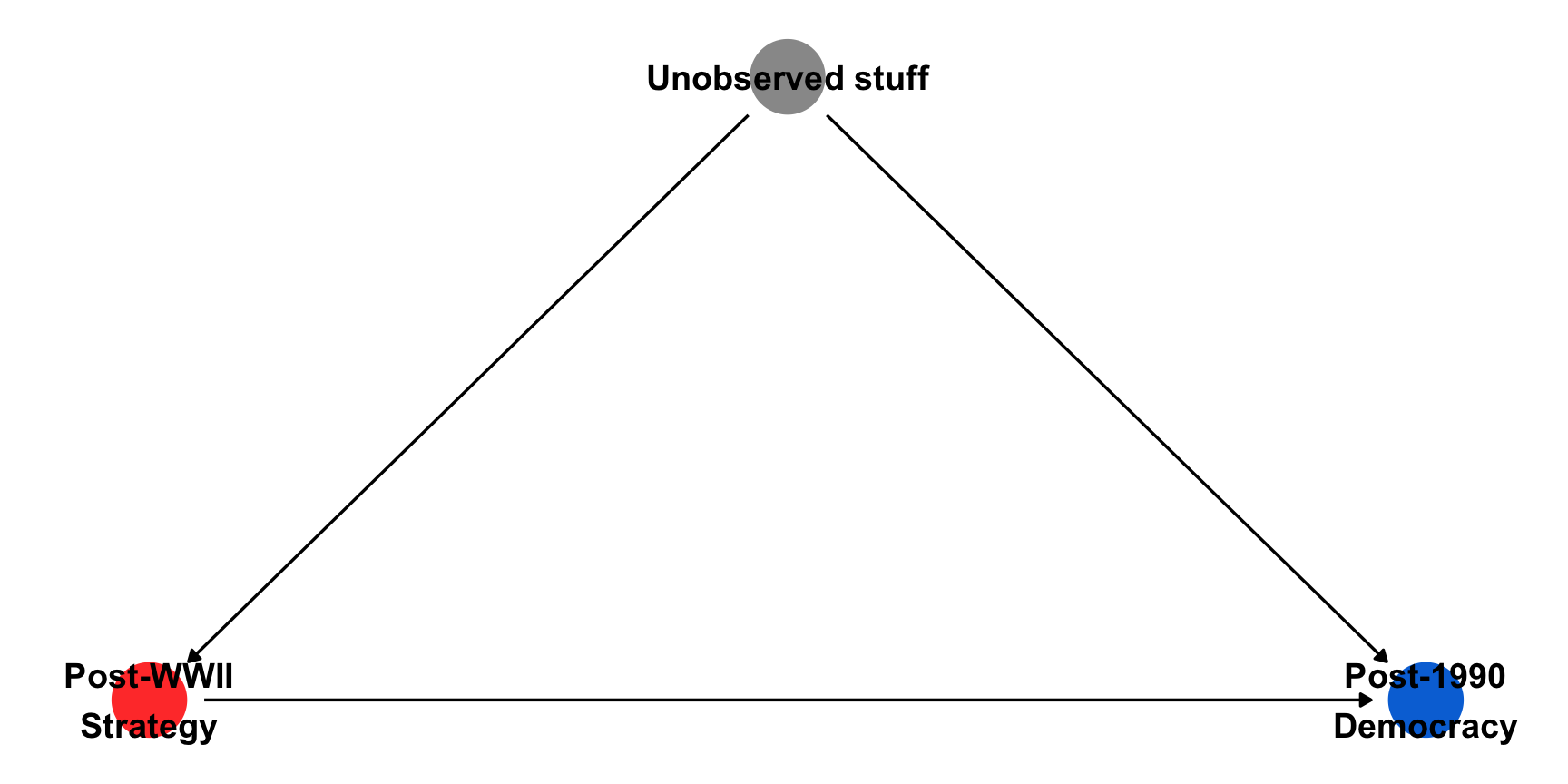
Final Project Essentials: Interaction Terms
Jeremy Springman
University of Pennsylvania
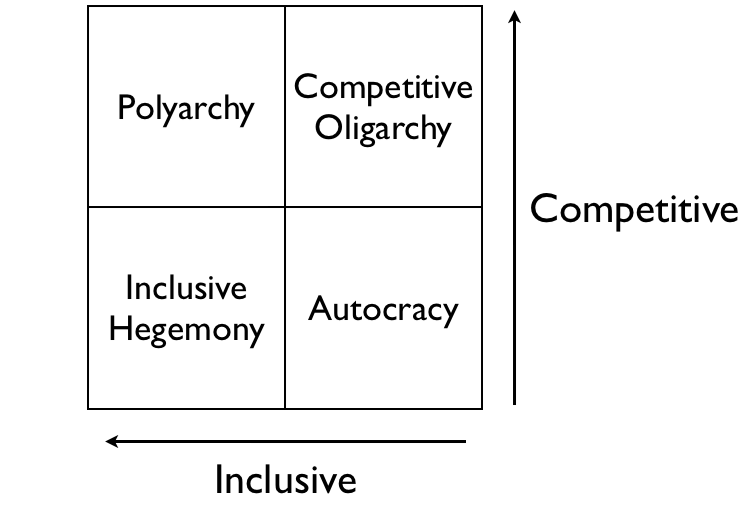
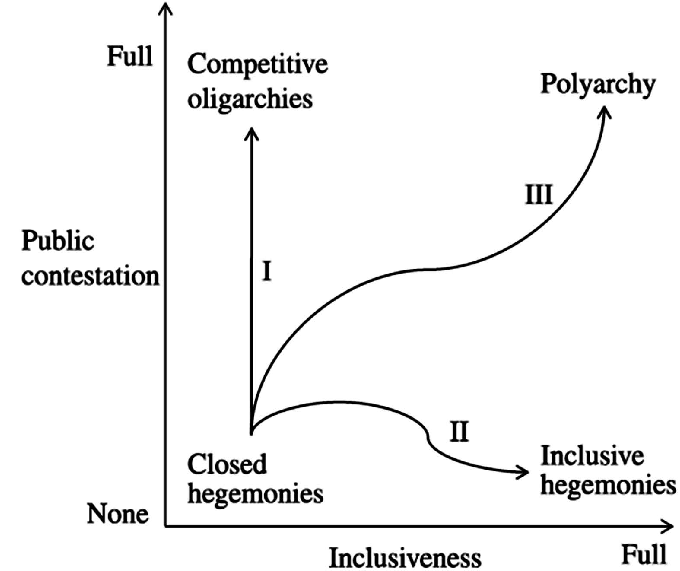
Polyarchy is about the degree of political competition
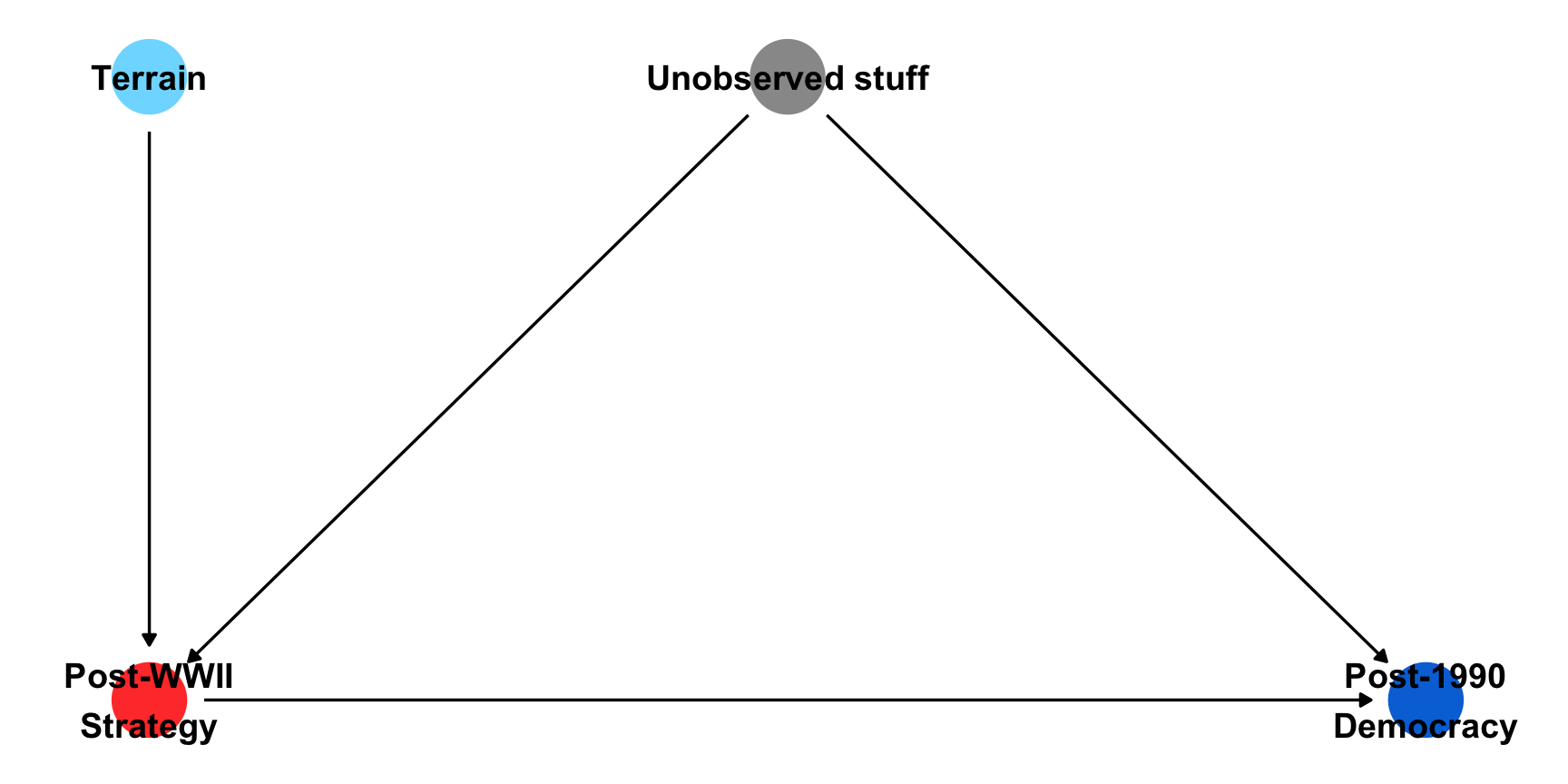
Causal effects of regime-type are difficult, but…
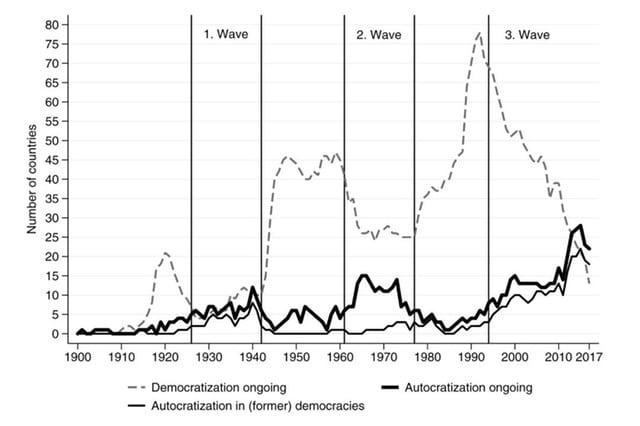
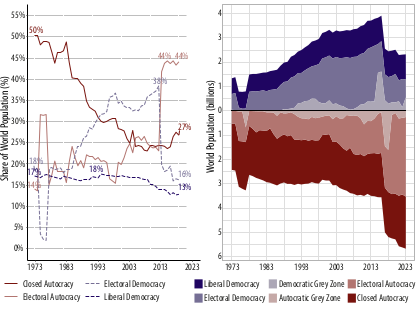
Ongoing transitions across regions
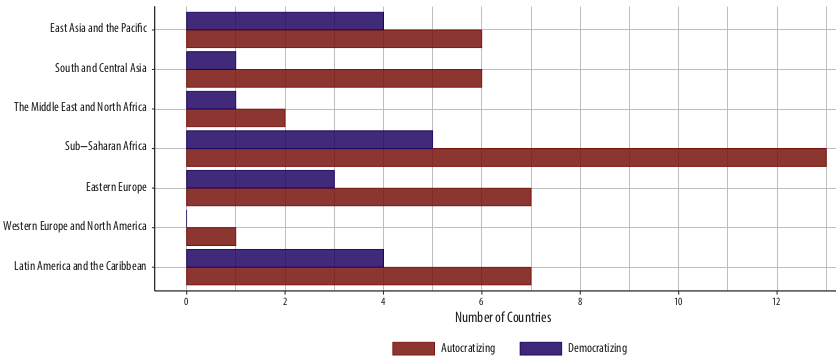
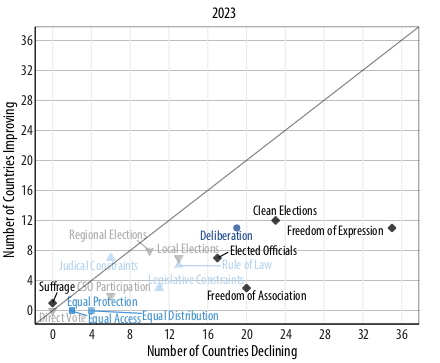
Most deterioration seen on:
Broad trends
What did you find interesting?
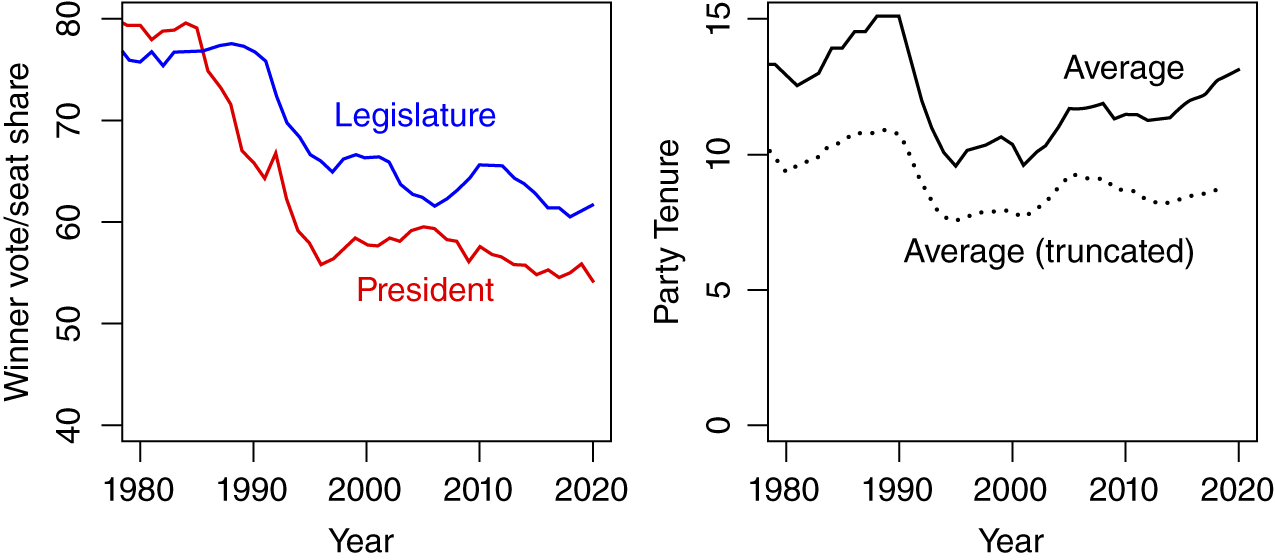
Incumbents are losing elections
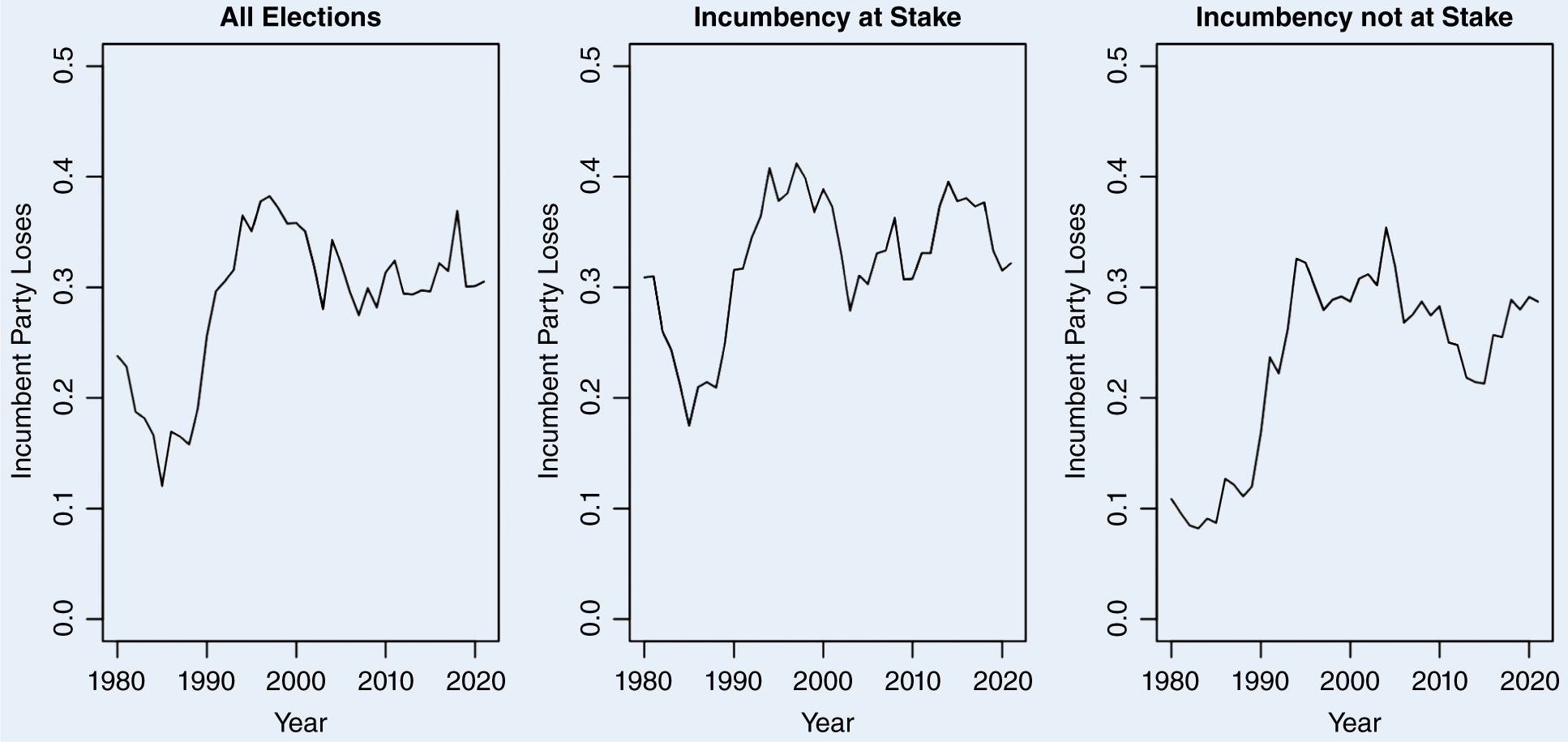
Incumbents are losing elections
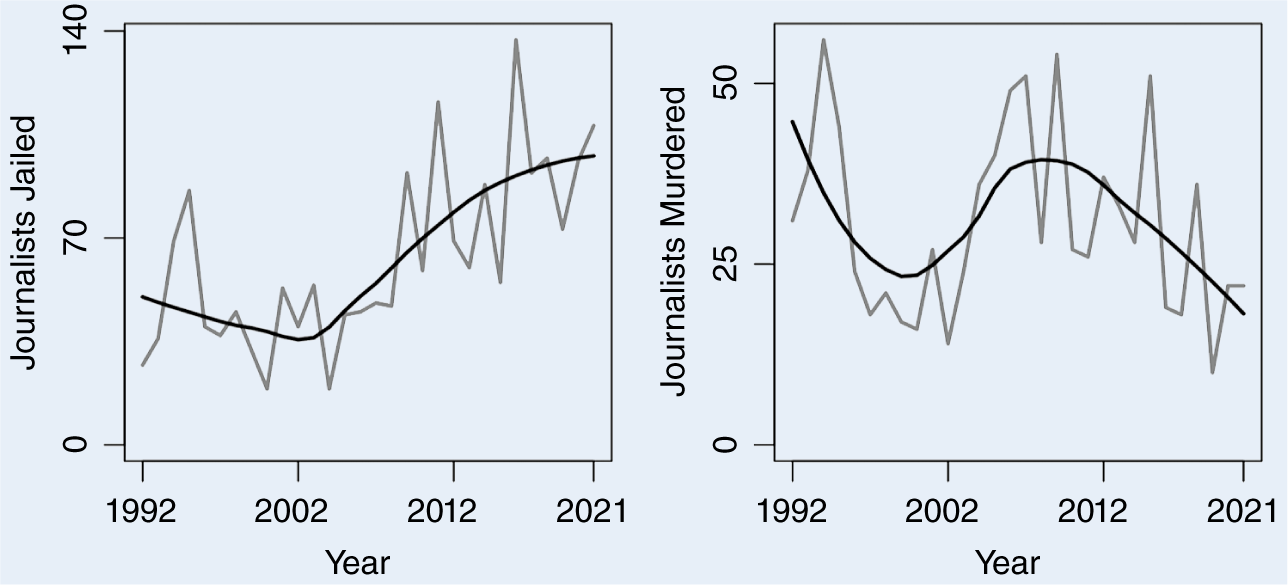
Mixed evidence on attacks on journalists
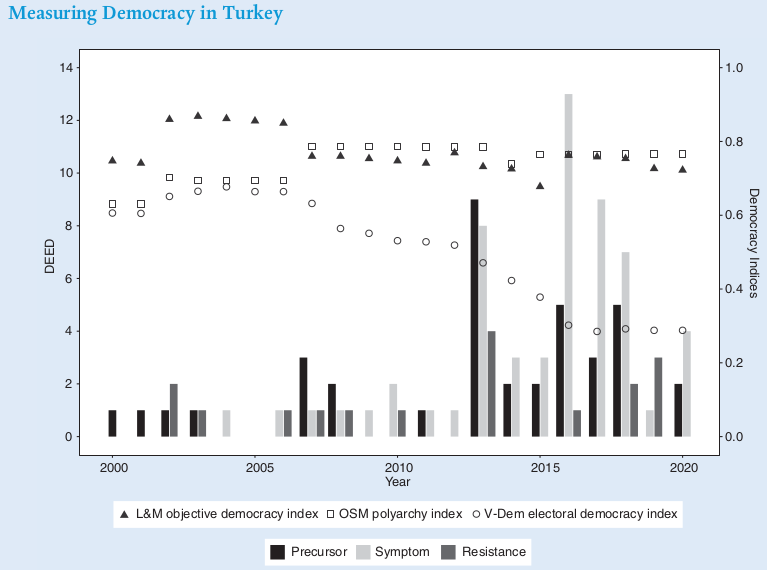
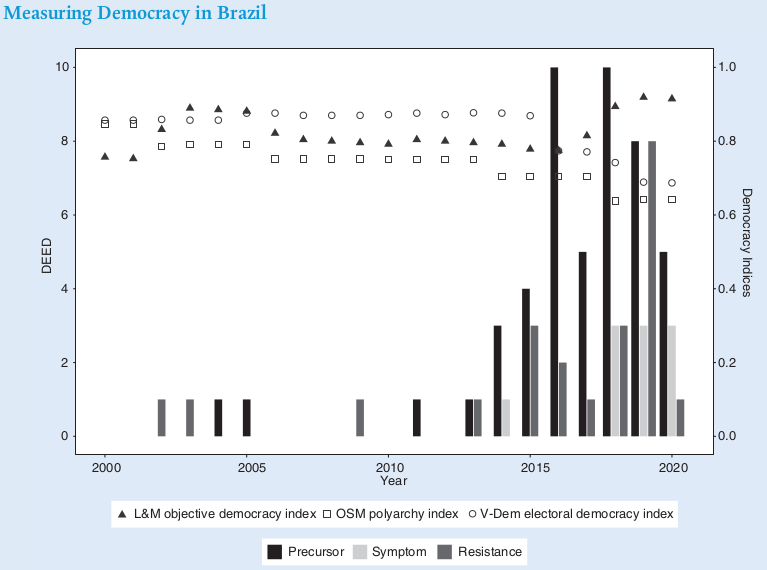
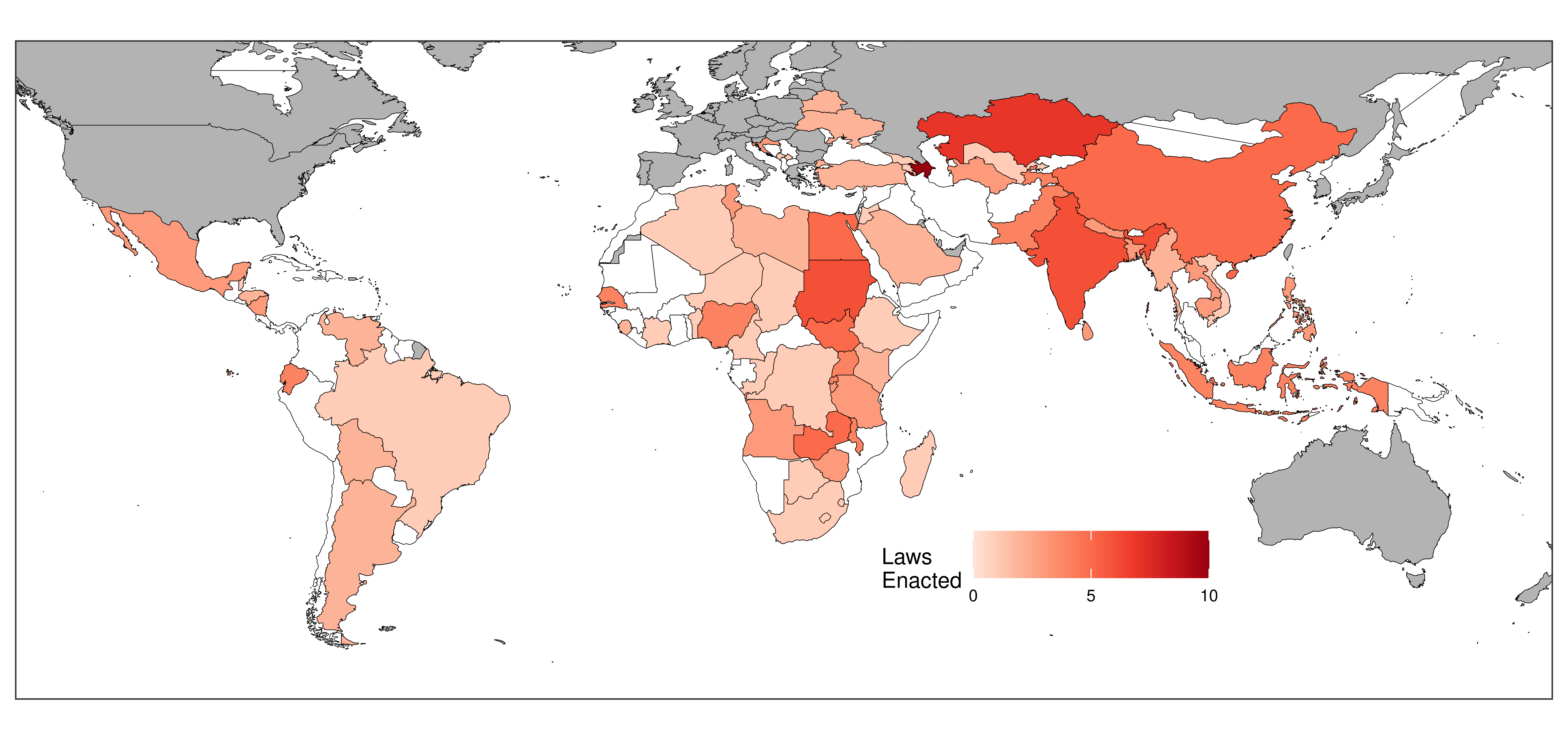
Lots of new anti-NGO laws
In Africa, democratization after the Cold War was shaped by the level of development (urbanization) at the start of countries’ anti-colonial movements
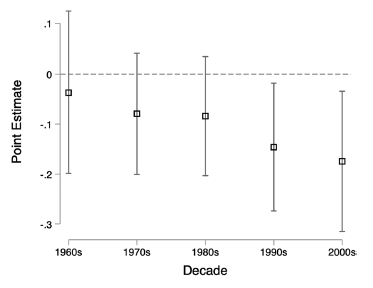
Why does opposition strategy affect democratization decades later?
Mechanisms:
Attaching package: 'ggdag'The following object is masked from 'package:stats':
filter
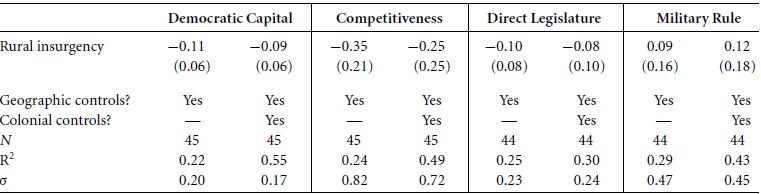
We do not seen an impact of Post-WWII Opposition Strategy on Post-1990 Institutions
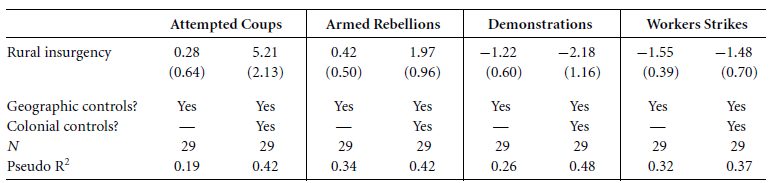
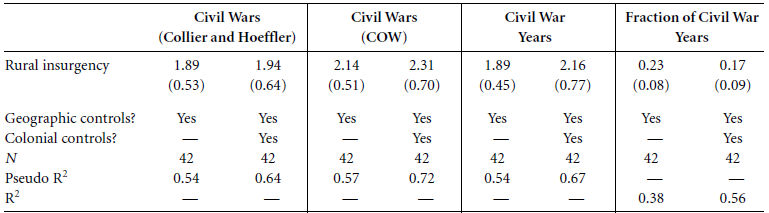
What is an interaction term?
\[ Y_i = \alpha + \beta_1 X_{i1} + \beta_2 X_{i2} + \beta_3 X_{i1}*X_{i2} + \epsilon_i \]
What are interaction terms used for?
Example: Continuous outcome with two binary predictors