Attaching package: 'ggdag'The following object is masked from 'package:stats':
filter
Final Project Essentials: Interaction Terms
Jeremy Springman
University of Pennsylvania
In Africa, democratization after the Cold War was shaped by the level of development (urbanization) at the start of countries’ anti-colonial movements
Why does opposition strategy affect democratization decades later?
Mechanisms:
Attaching package: 'ggdag'The following object is masked from 'package:stats':
filter
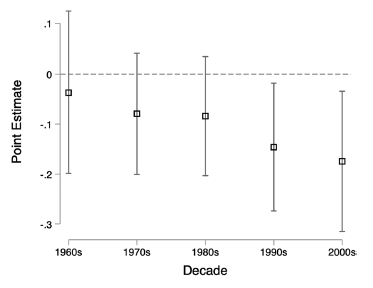
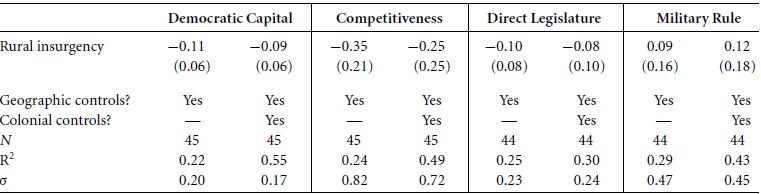
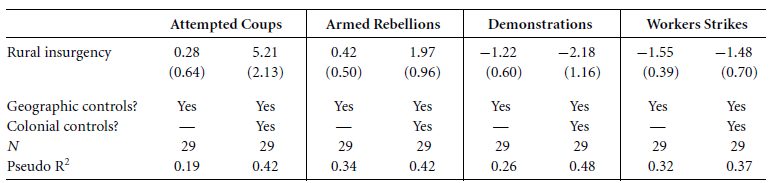
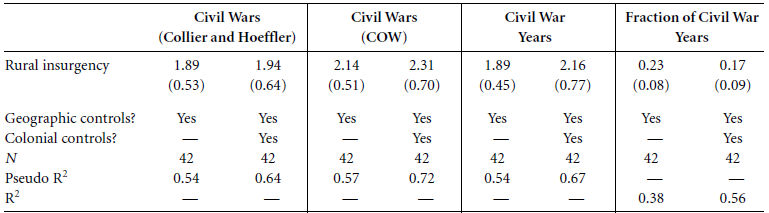
We do not seen an impact of Post-WWII Opposition Strategy on Post-1990 Institutions

Strategies of Control
Moments of uncertainty about political opportunity
Political moment
Treatment
Year = c(0,1,2,3)
Outcome = c(NA, 1.3, 1.5, 1.7,
1, 1.2, 1.4,1.6,
1.1, 1.3, 1.7, 1.9)
Treatment = c("Comparison","Comparison","Comparison","Comparison",
"Control", "Control","Control","Control",
"Treatment", "Treatment", "Treatment", "Treatment")
dat = data.frame(Year, Outcome, Treatment)
dat$Treatment = factor(dat$Treatment, levels = c("Treatment", "Comparison", "Control"))
ggplot(data = dat, aes(x = Year, y = Outcome, color = Treatment)) +
geom_line(aes(linetype=Treatment),size=2) +
geom_point(size = 6) +
ylim(0.8, 2.2) +
scale_linetype_manual(values=c("solid", "dotted", "solid")) +
scale_color_manual(values = c("blue", "black", "red" ) ) +
theme(legend.position = c(0.8, 0.2), text = element_text(size=20),
legend.title=element_blank())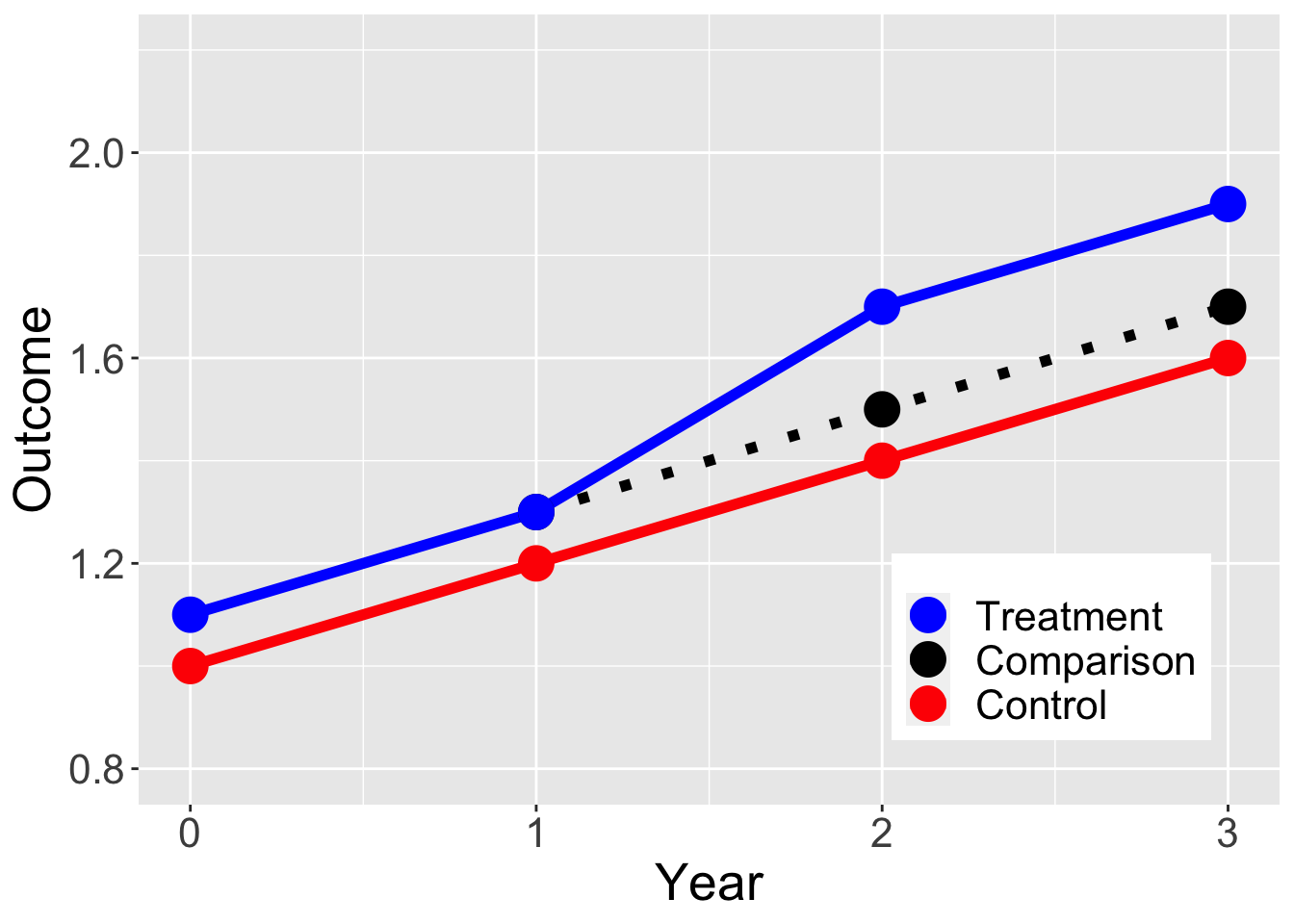
What is an interaction term?
What are they used for?
How do they do work?
\[ Y_i = \alpha + \beta_1 X_{i1} + \beta_2 X_{i2} + \beta_3 (X_{i1}*X_{i2}) + \epsilon_i \]
Example: Continuous outcome with two binary predictors