Accountability and Information 1
Final Project Essentials: Fixed Effects
Logistics
Assignments
- Today
- Tuesday (3/26)
- Jablonski and Seim (2023)
- Questions about Data Assignment 1
- Thursday (3/28)
- Data Assignment 1 Due
- Readings on Accountability and Information
Agenda
- de la Sierra (2020)
- Final Project Essentials: Interaction terms and Fixed Effects
- Data Assignment 1
de la Sierra (2020)
Background
What is political accountability?
- Answerability
- Enforceability
Background
What is a state?
- An entity with a monopoly on the legitimate use of physial violence
- Capacity to act as the sole arbiter and enforcer of law and order
Background
What are a state’s essential functions?
- War making: eliminating external rivals
- State making: Eliminating internal rivals
- Protection: Protecting clients
- Extraction: Acquiring resources
Background
State formation
- States have their origins as armed actors
- The most successful armed actors became states
- Where armed actors establish states depends on their ability to tax
- Taxation induces proto-accountability: more wealthy people means more tax revenue
- States lead to the emergence of growth
What is the distinction between roving and stationary bandits?
Background
The resource curse
- Abundant natural resources are associated with lower growth, more conflict, and worse human outcomes?
- Why might abundant natural resources reduce political accountability?
Theory
Observability and incentives
- Taxation requires providing protection and establishing a monopoly of violence
- If production can be observed, a higher value of output increase returns to taxing production where output is produced (direct)
- If production can’t be easily observed, a higher value of output increases returns to taxing production through people and consumption (indirect)
- Taxing people requires more sophisticated administration (capacity) and
Data
Sample
- Panel data on village histories (1995-2013)
- 650 locations
Outcomes
- State formation: Stationary bandit, output taxation, sophisticated taxation, security services, fiscal and judicial administration
- Population welfare: Savings, weddings, migrants
Research Design
- Demand shocks for two resources
- Coltan is observable
- Gold is not observable
- Exogenous timing of mineral price changes
Findings
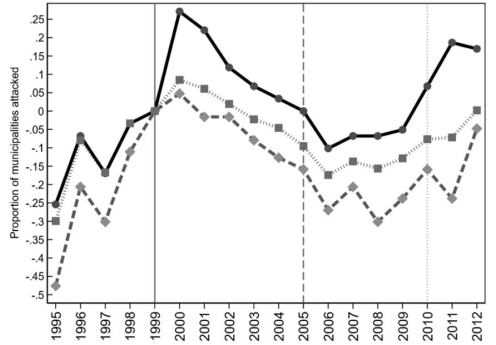
Findings
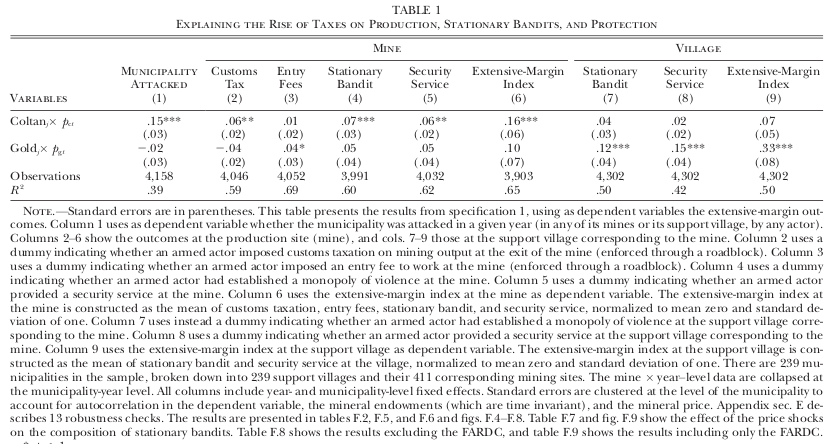
Findings
- Coltan prices:
- Increase stationary bandits, security at mines (not villages), simple taxation, and welfare (militia only)
- Decrease fiscal and judicial administration
- Gold prices:
- Increase stationary bandits, security at villages (not mines), sophisticated taxation, fiscal and judicial administration, and welfare (army or militia)
- Stationary bandits increase HH welfare if the value of the protection they provide outweighs the distortionary effect of their taxation
Policy Implications
Jablonski and Seim (2023)
Final Project Essentials
Interaction Terms
What is an interaction term?
- Simple linear models assume that the effect of predictors is independent of other factors
- Interaction terms allow us to estimate the difference in the slope of a predictor across unit characteristics
What are they used for?
- Heterogeneous effects
- Difference-in-differences
Interaction Terms
How do they do work?
\[ Y_i = \alpha + \beta_1 X_{i1} + \beta_2 X_{i2} + \beta_3 (X_{i1}*X_{i2}) + \epsilon_i \]
Example: Continuous outcome with two binary predictors
- \(\alpha\): Intercept when \(X_{i1}\) and \(X_{i2}\) are 0
- \(\beta_1\) Slope when \(X_{i2} = 0\)
- \(\beta_2\) Difference in \(\alpha\) between \(X_{i2}=0\) and \(X_{i2}=1\)
- \(\beta_3\) Difference in \(\beta_1\) between \(X_{i2}=0\) and \(X_{i2}=1\)