Foreign Aid 1
Logistics
Assignments and Upcoming
- Today
- Wednesday (4/9)
- More foreign aid readings
- Data Assignment 1 (due Friday)
- Monday (4/14)
- Foreign Aid Obituary
- Feedback on FP Extension
Agenda
- Finishing up interaction terms
- Overview of Foreign Aid
- Briggs (2016)
- Briggs (2021)
- Data Assignment 1
Finishing up interaction terms
Interaction Terms
\[ Y_i = \alpha + \beta_1 X_{i1} + \beta_2 X_{i2} + \beta_3 X_{i1}*X_{i2} + \epsilon_i \]
Example: Continuous outcome with two binary predictors
- \(\alpha\): Intercept when \(X_{i1}\) and \(X_{i2}\) are 0
- \(\beta_1\): Slope when \(X_{i2} = 0\)
- \(\beta_2\): Difference in \(\alpha\) between \(X_{i2}=0\) and \(X_{i2}=1\)
- \(\beta_3\): Difference in \(\beta_1\) between \(X_{i2}=0\) and \(X_{i2}=1\)
Overview of Foreign Aid
Aid Disbursements
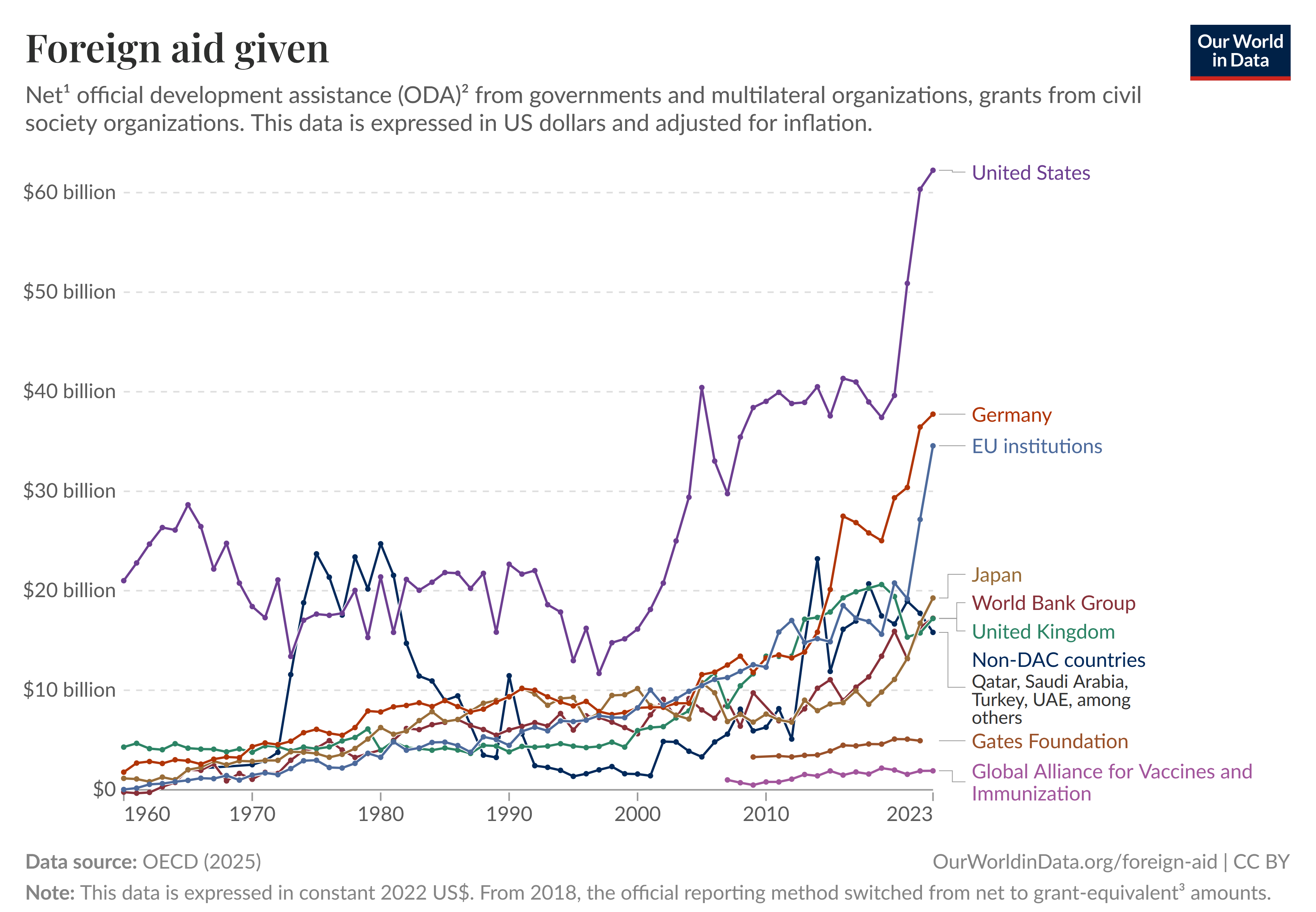
Aid Disbursements
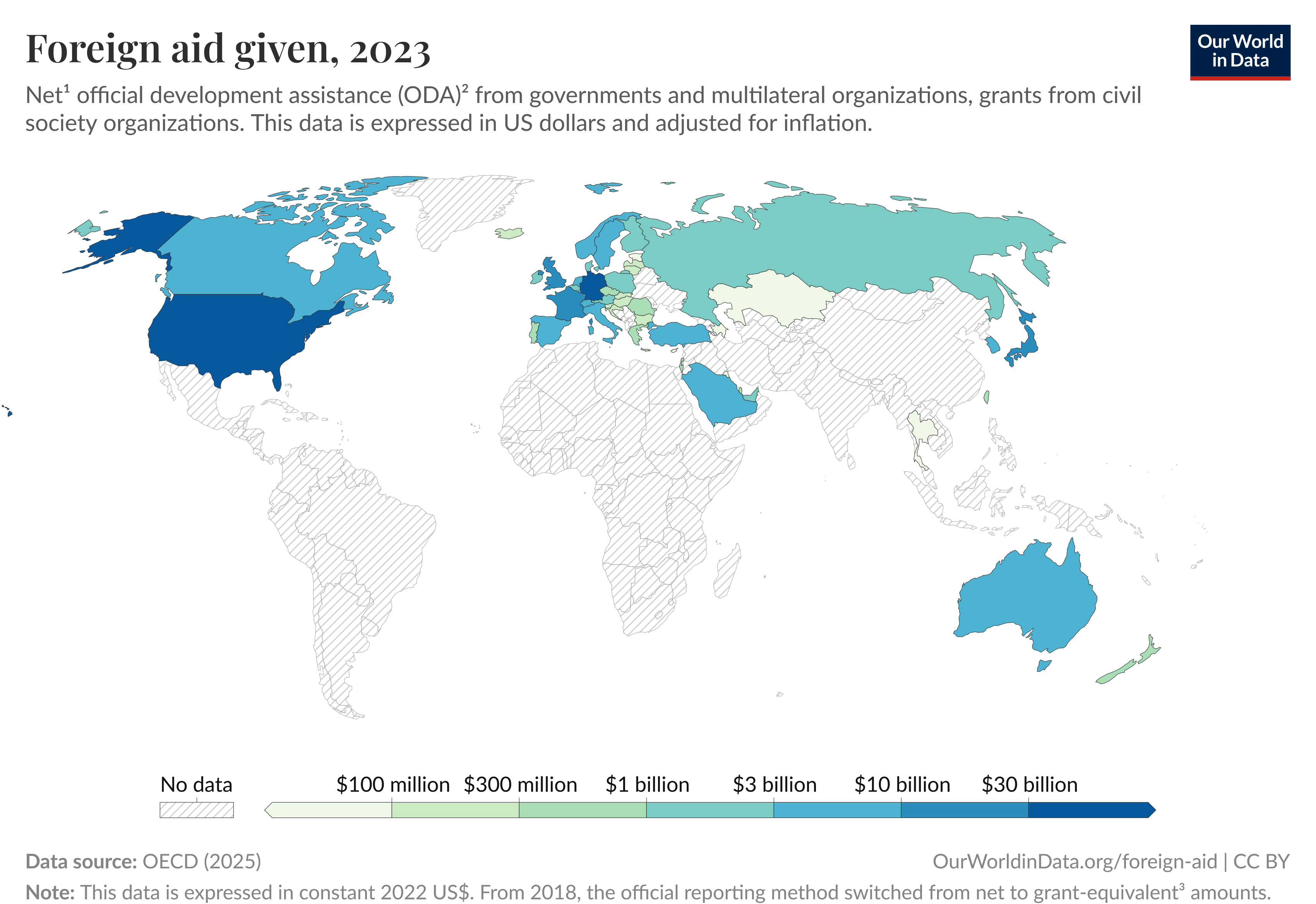
Aid Disbursements
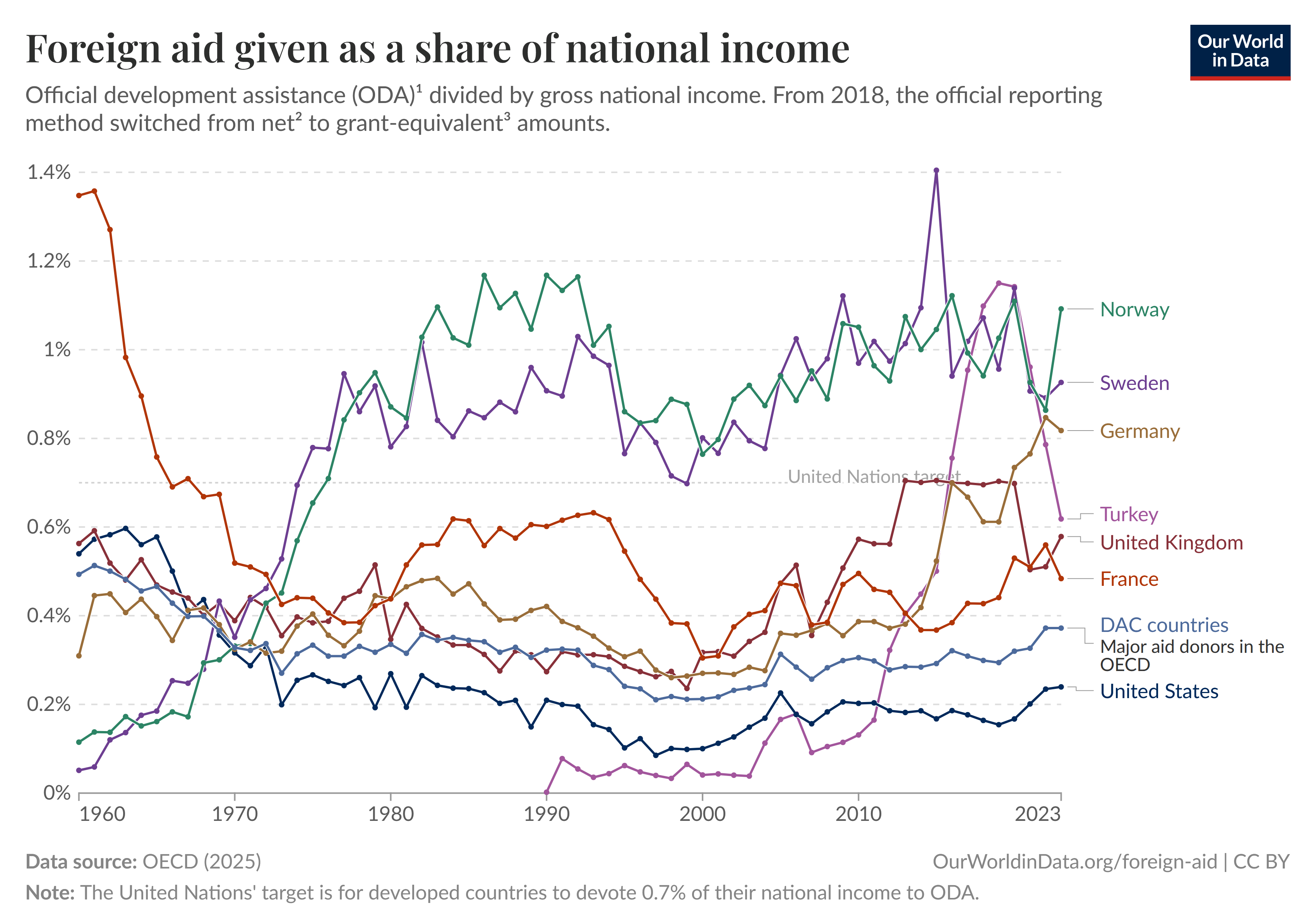
Aid Disbursements
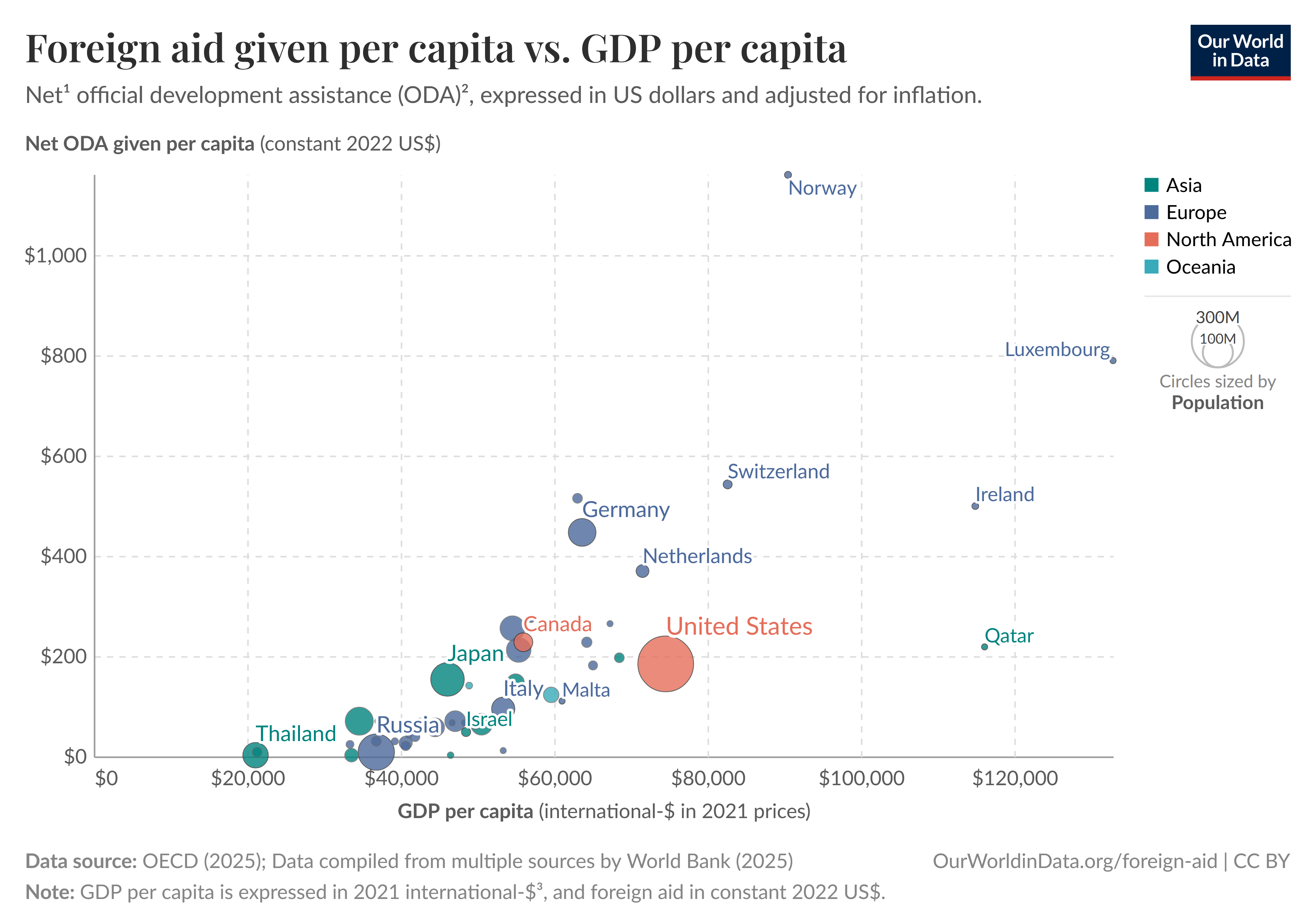
Aid Disbursements
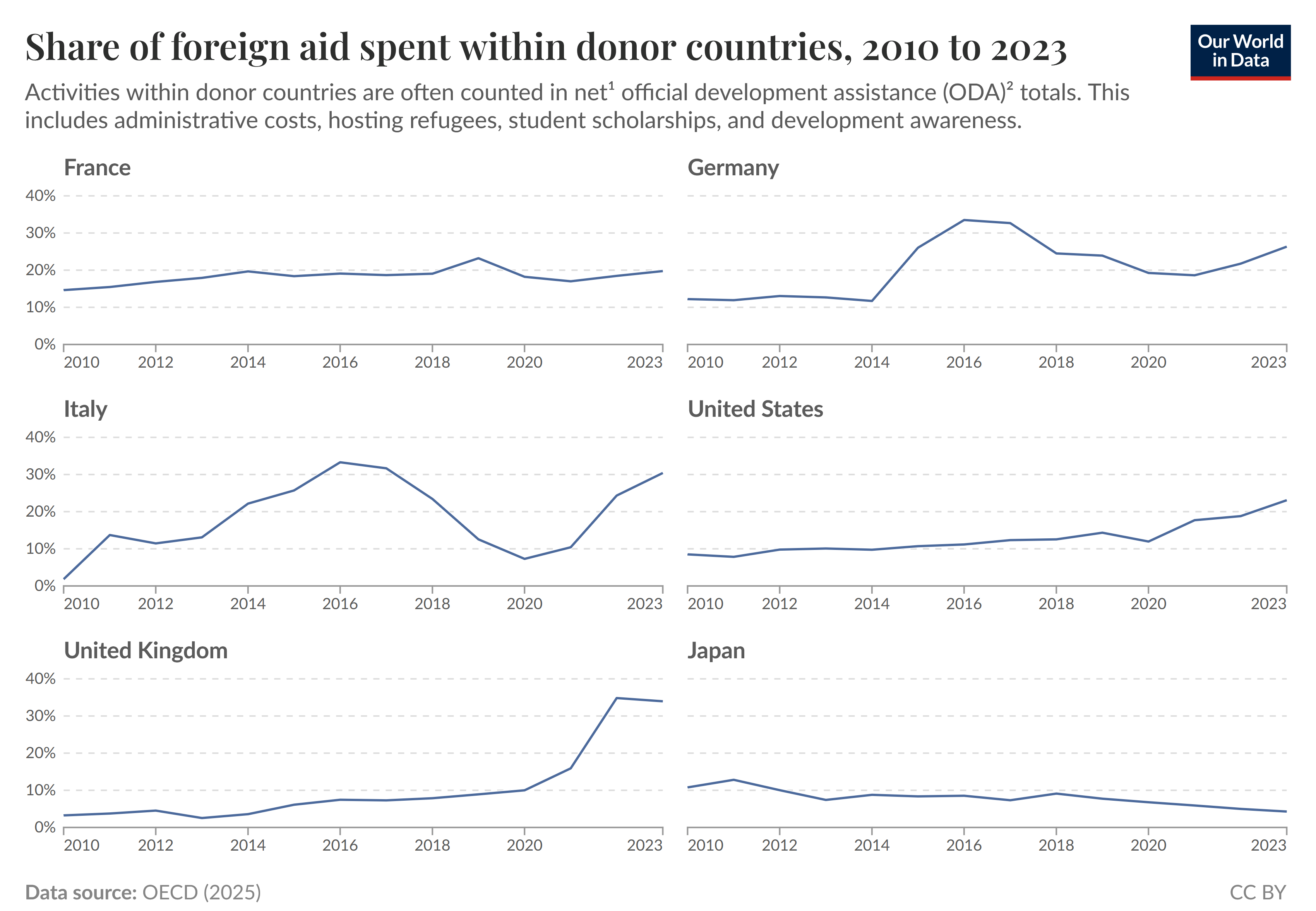
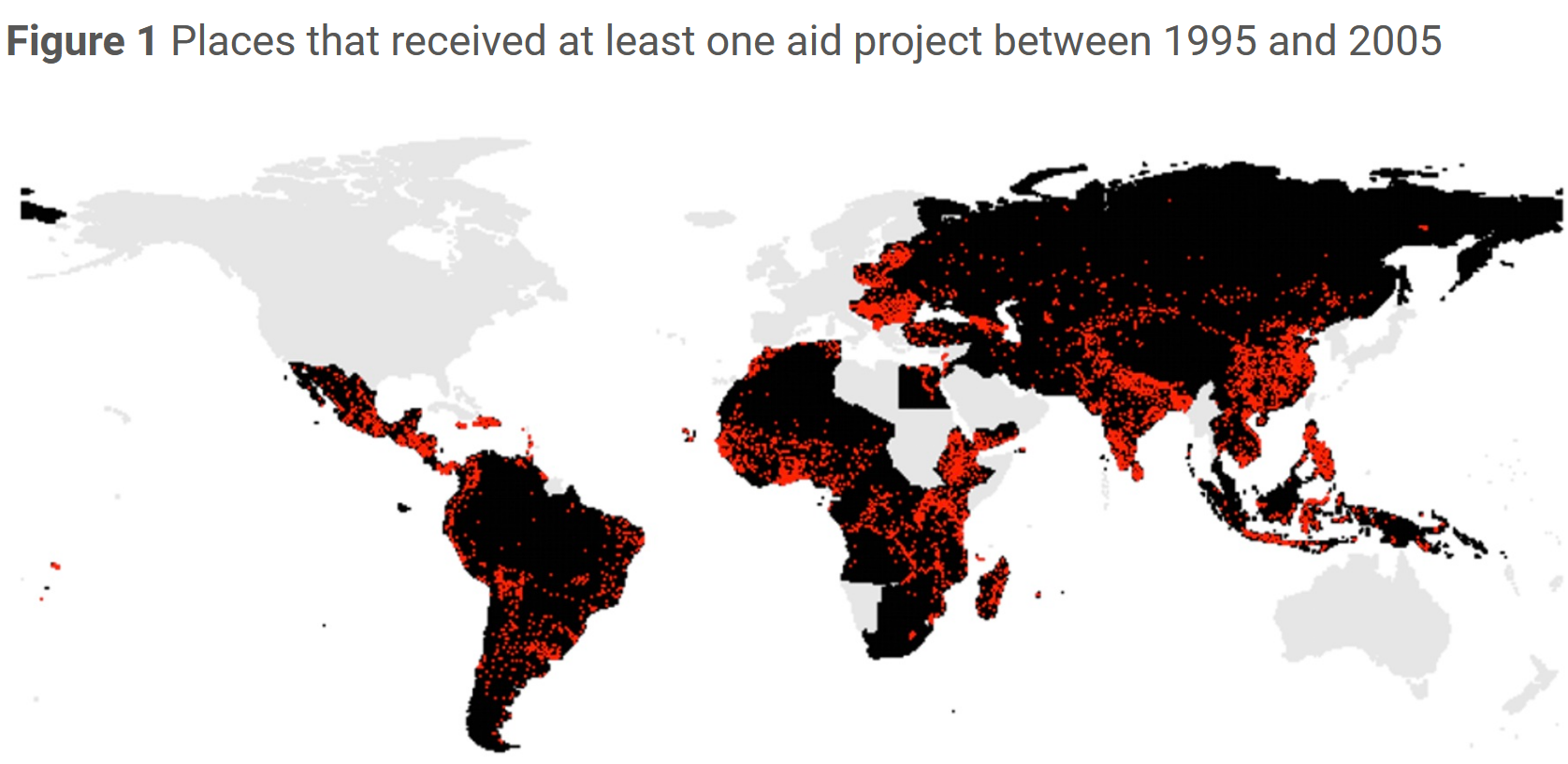
Aid Received
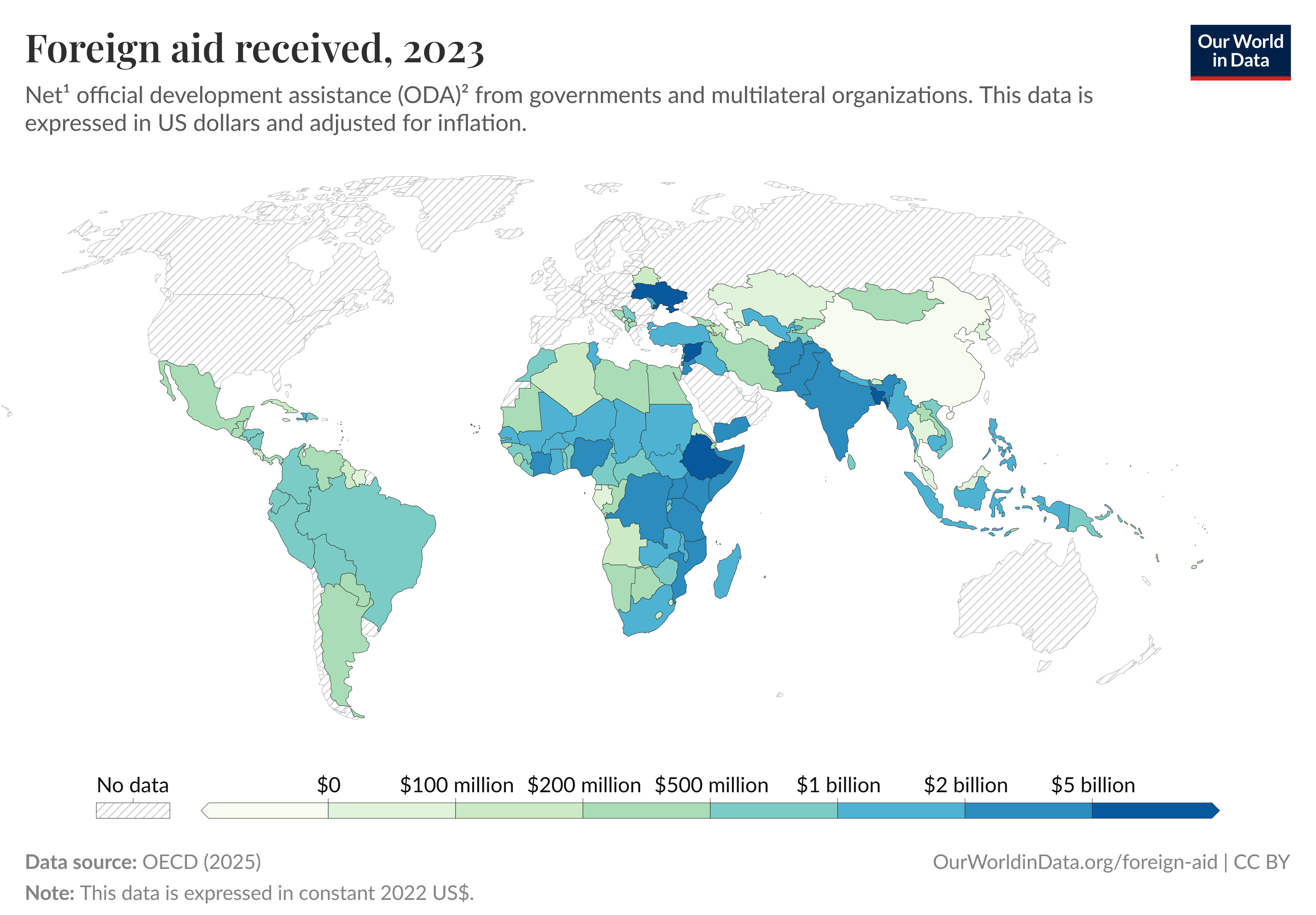
Aid Received
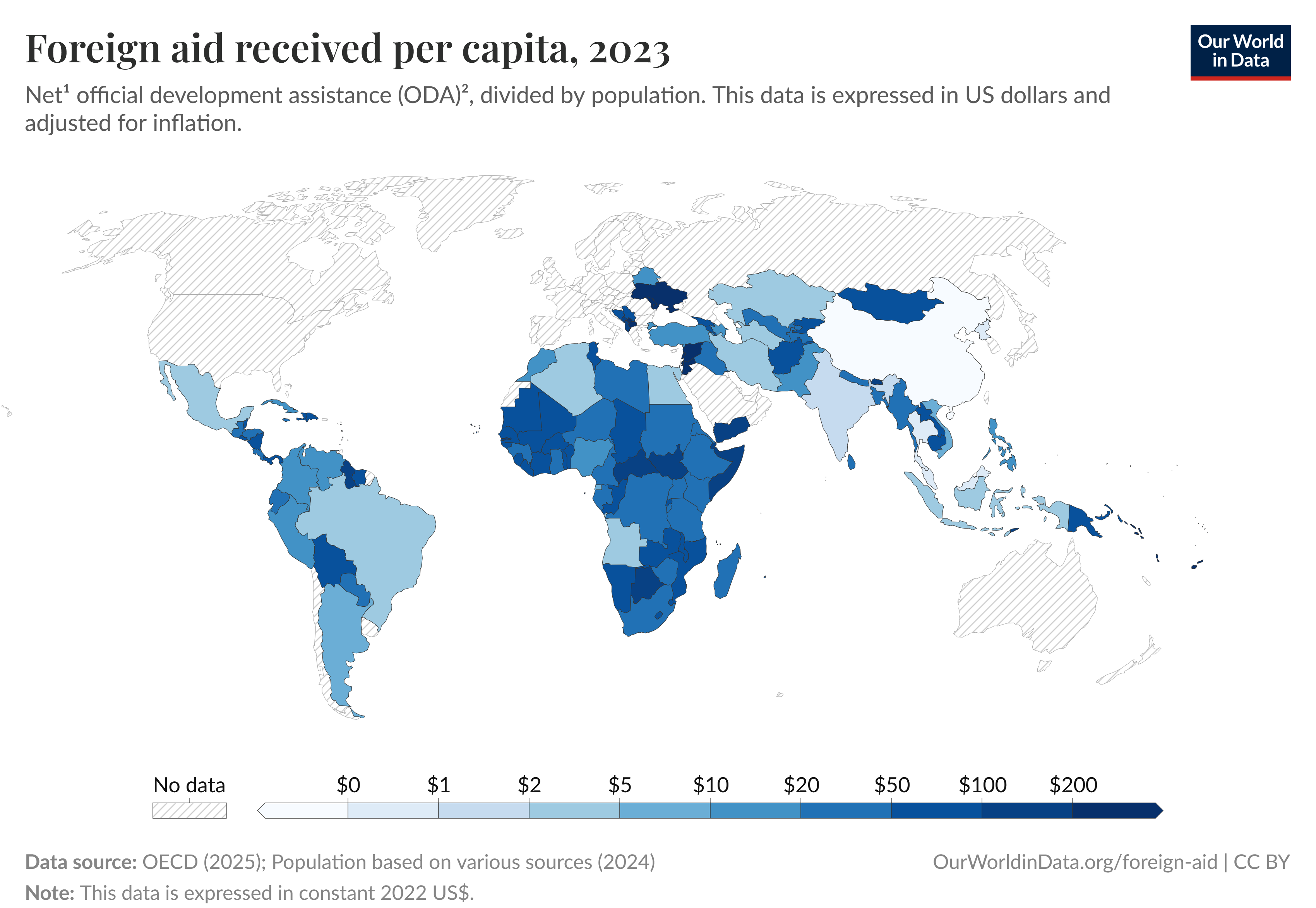
Aid Received
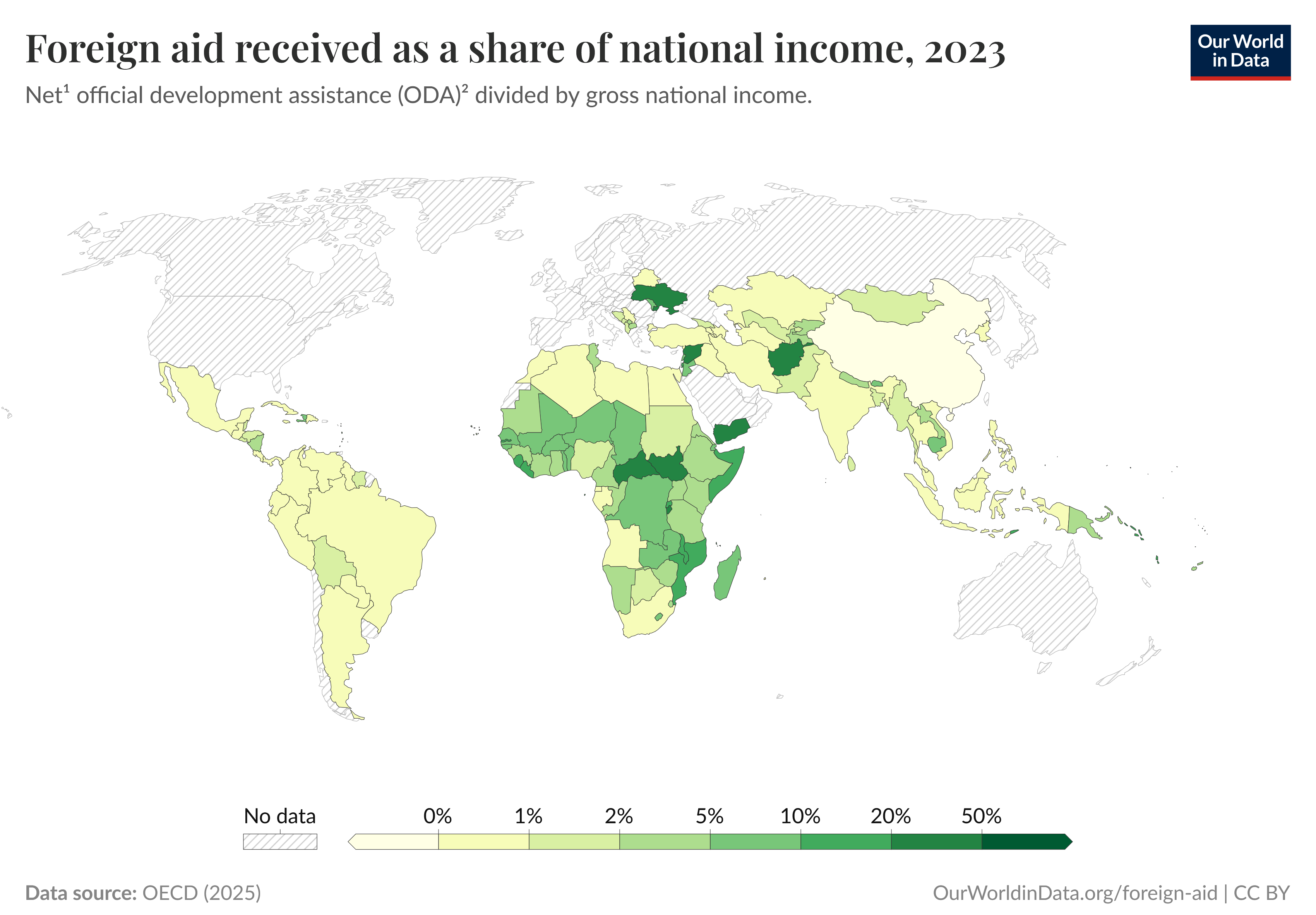
Aid Received
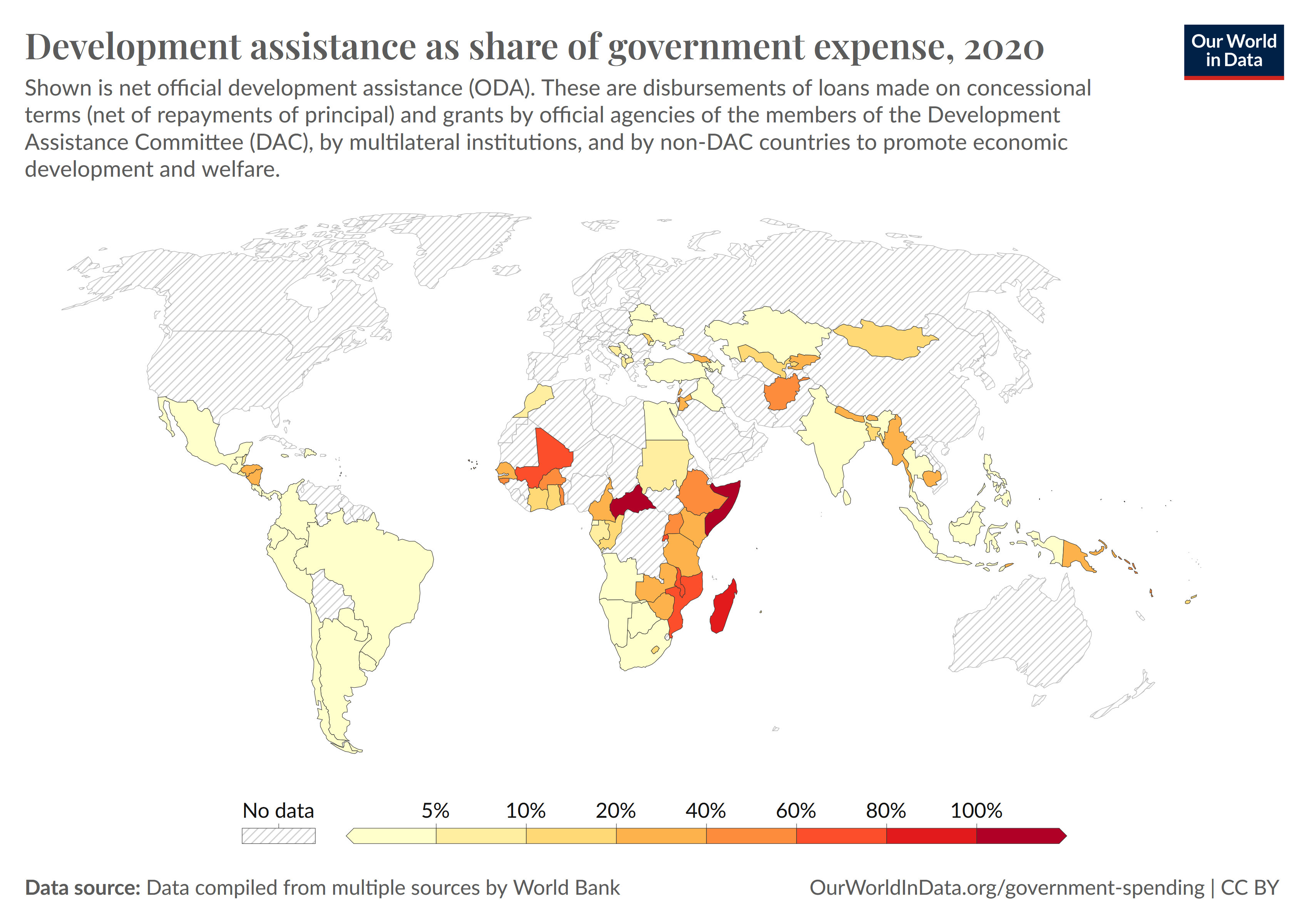
Aid Received
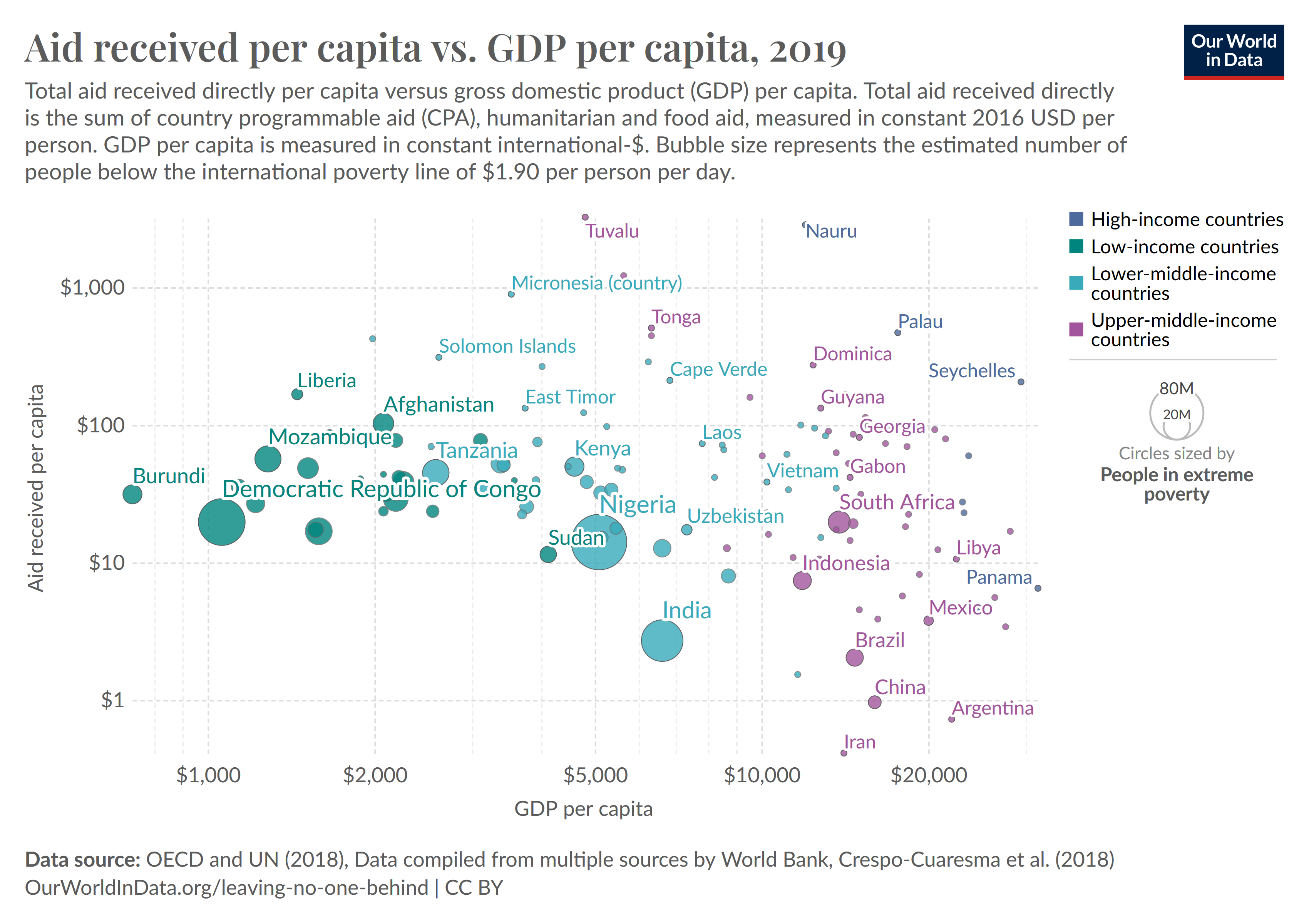
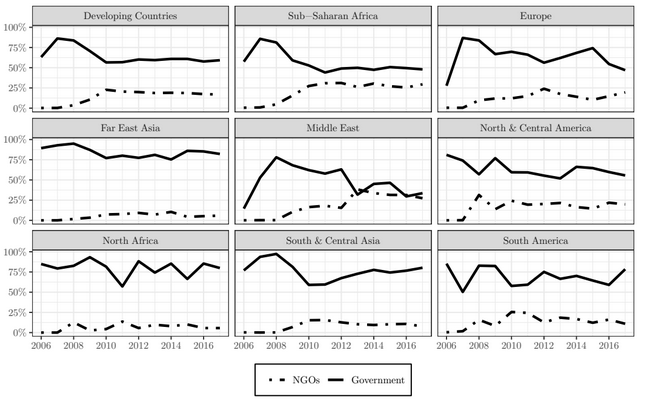
Aid Distribution
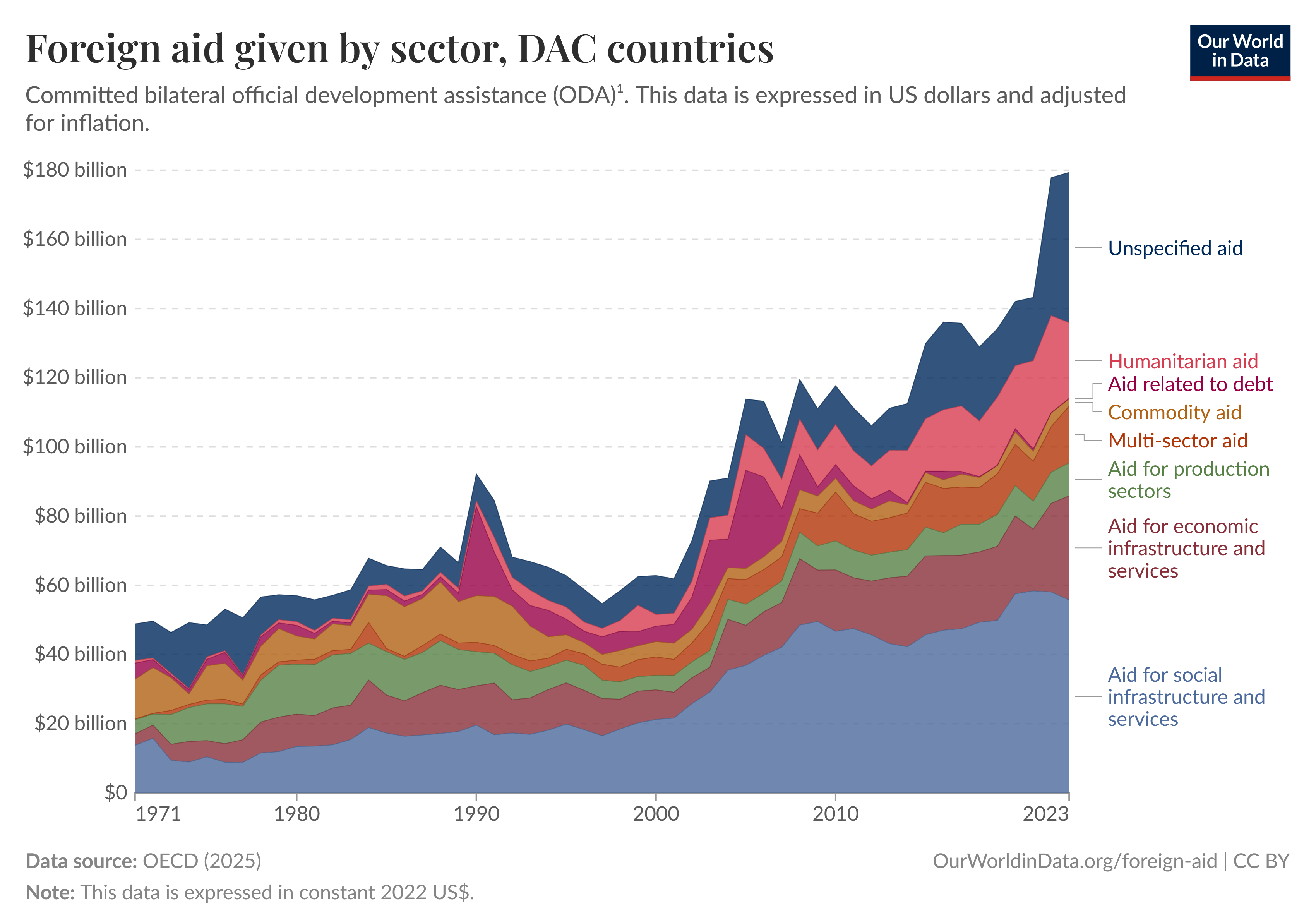
Aid Impacts
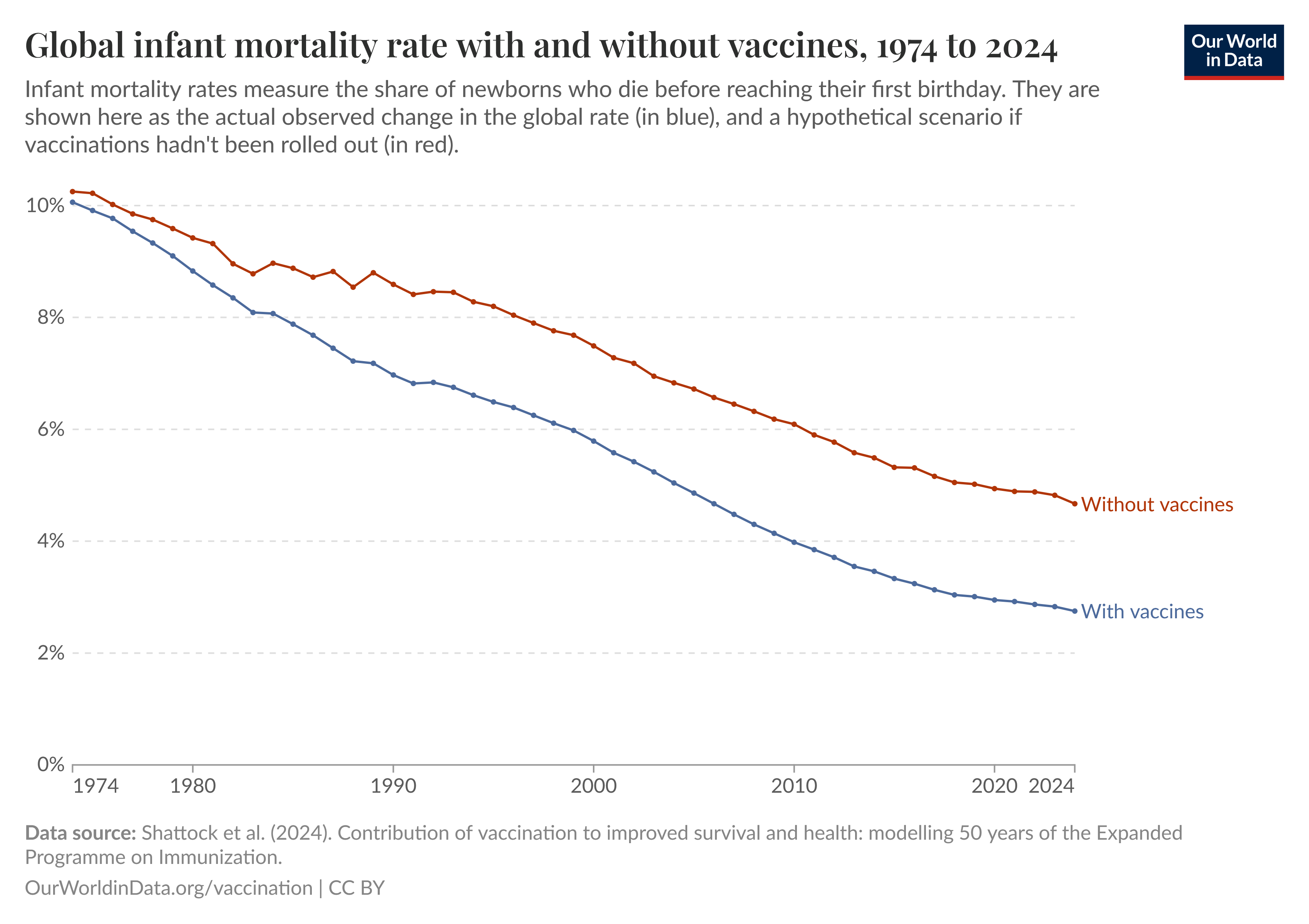
Aid Impacts
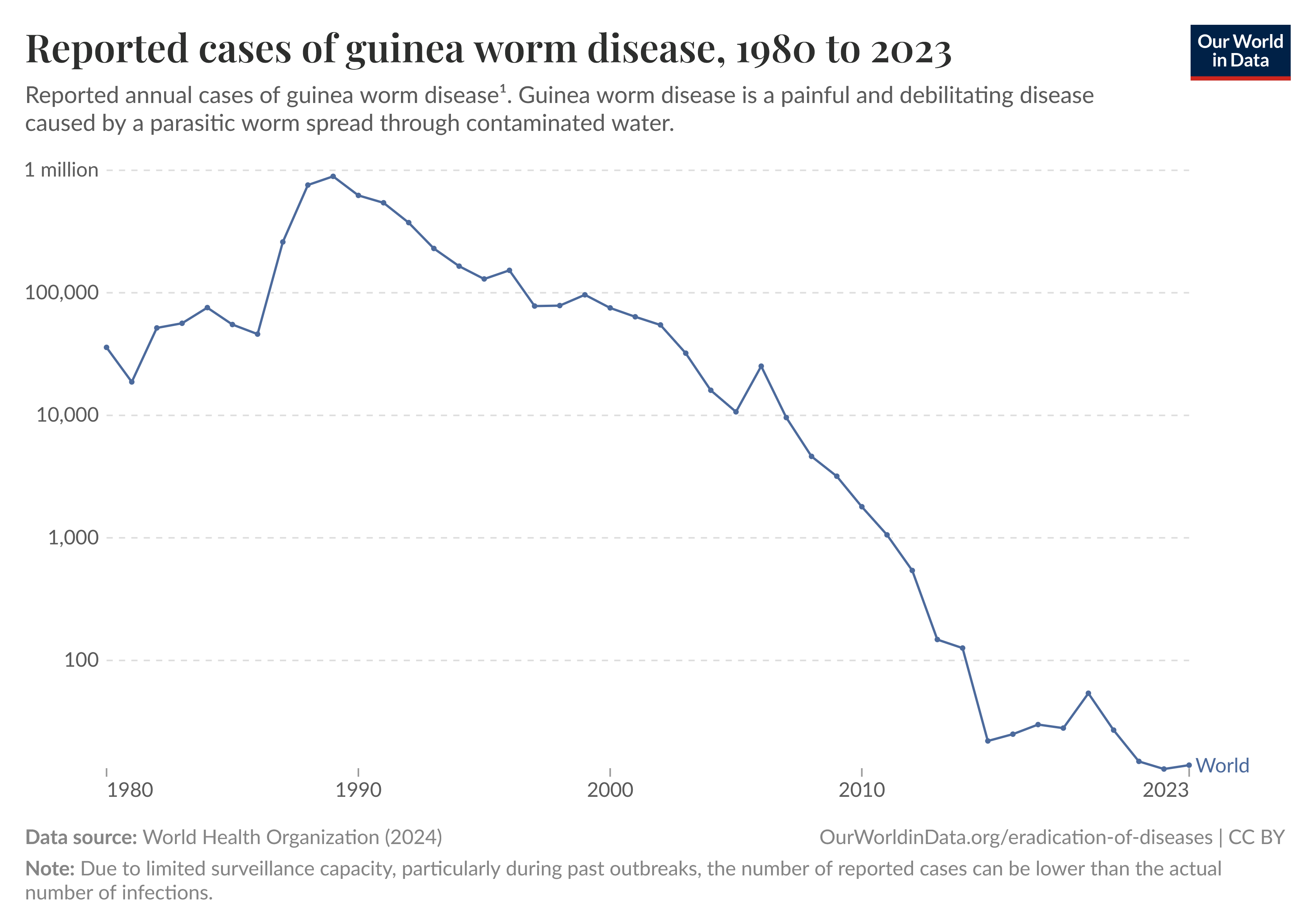
Aid Impacts
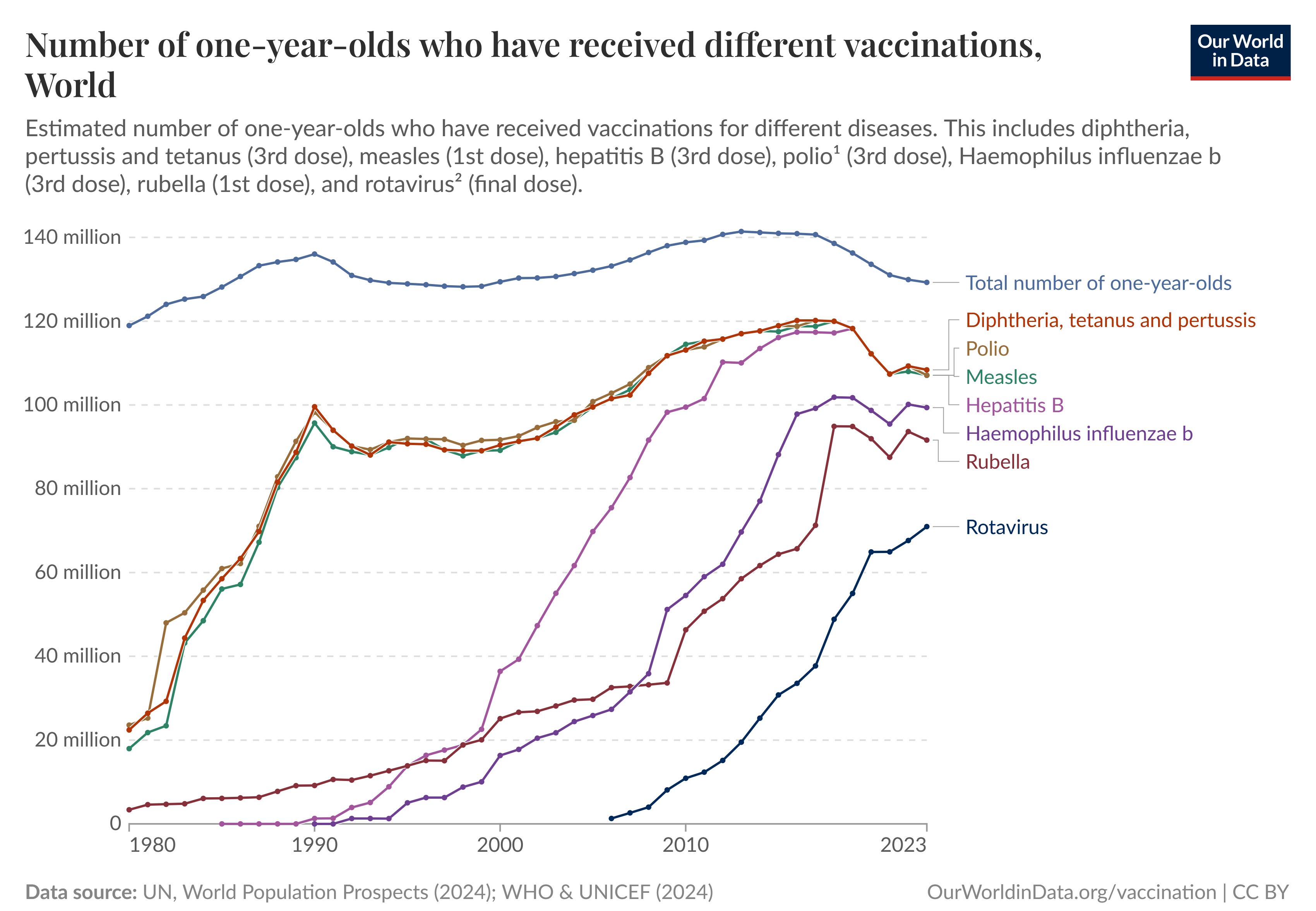
Aid Impacts
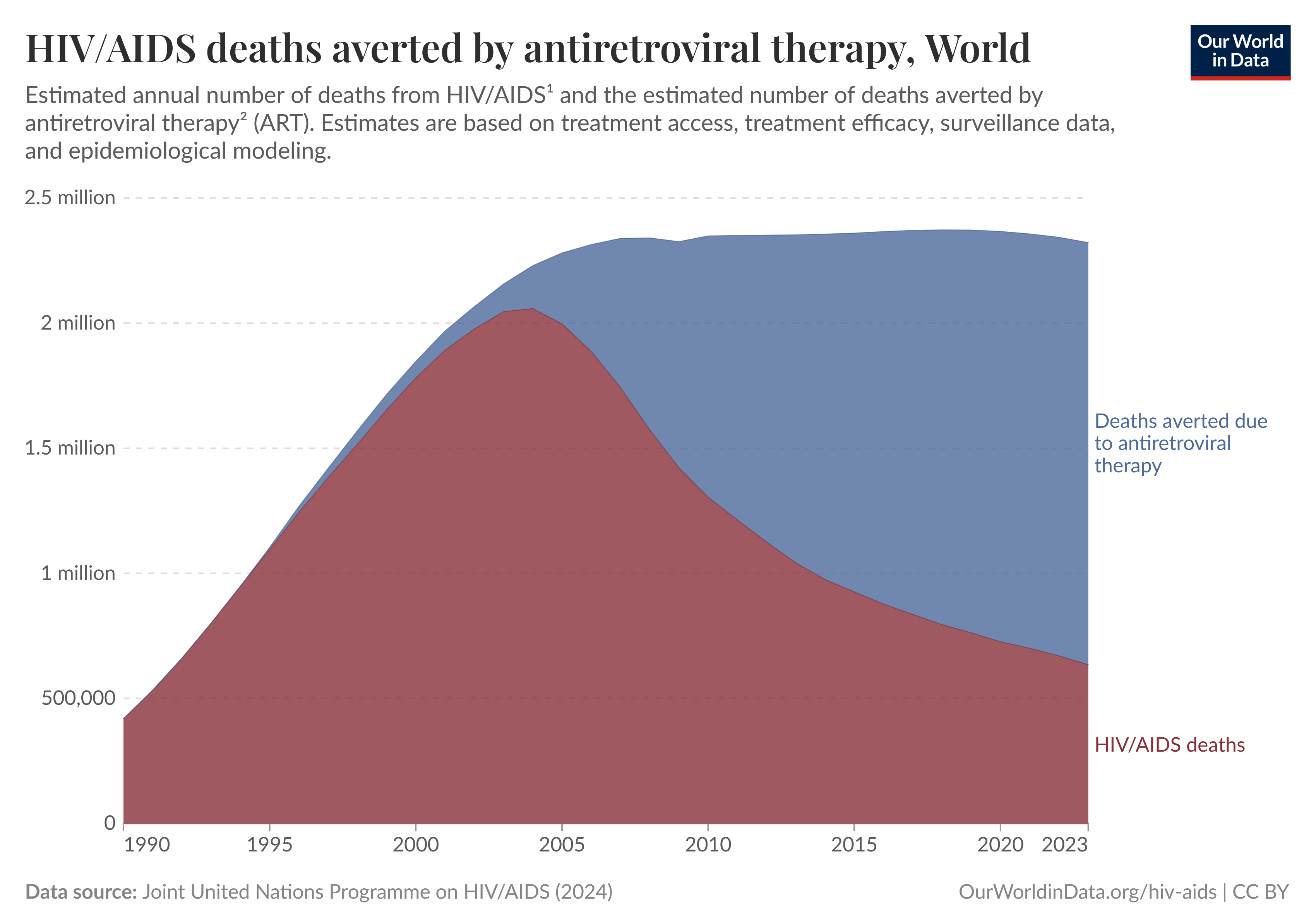
Debates Around Aid
- Economic growth
- Welfare
- State capacity
- Poverty alleviation
- Accountability
Debates Around Aid
- Budget support vs Project Aid
- Governments have information advantages
- Government budgets are subject to massive leakage (Reinikka & Svensson, 2004)
- Accountability
- Fungibility
- Donor vs recipient control
Aid Distribution
Briggs (2016)
Research Question
Is development aid targeted to the poorest citizens?
- Donors have a stated preference for using aid to alleviate extreme poverty
- Pressure may undermine this targeting
- Donor foreign policy objectives
- Donor ignorance
- Recipient politics
Theory
Why is it easier for multilateral donors to send aid to poorer countries?
- Multiple stakeholders mean aid must flow to places where preferences overlap
- Donor preferences are likely to overlap in the places with the greatest need
Case Selection
Most likely scenario for effective targeting:
- Commitments rather than disbursements
- Multilateral donors
- Project aid
Project aid must be proximate
- Aid is typically providing local public goods
Measurement
- DV: Aid projects per region
- World Bank and ADB 2009-2010
- Each region’s share (with and without cost weights)
- Total dollar value
- IV: Wealth quintiles
- DHS 1999-2008
- Relative wealth composition of each region (% of each quintile living in each region)
Research Design
- Unit Fixed Effects
- Lagged IV \(\rightarrow\) DV
- Control for obvious pre-treatment confounders
- What is his “most likely” design?
- Does he “identify” causal effects?
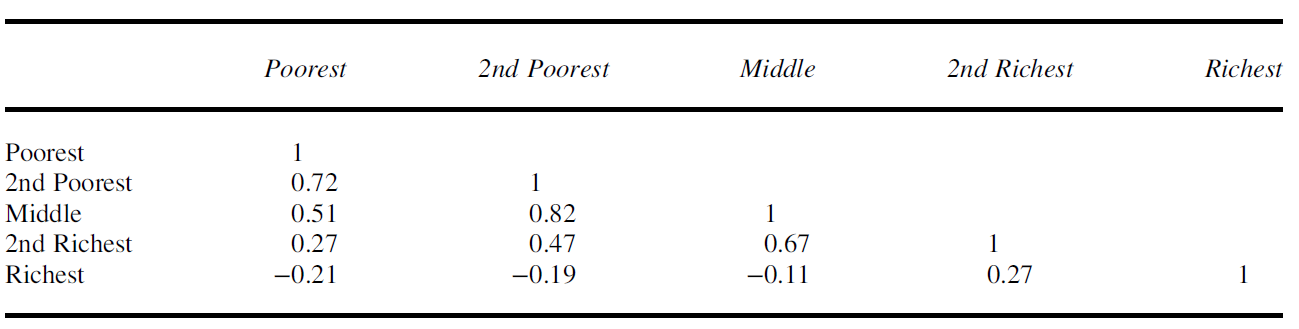
Measurement
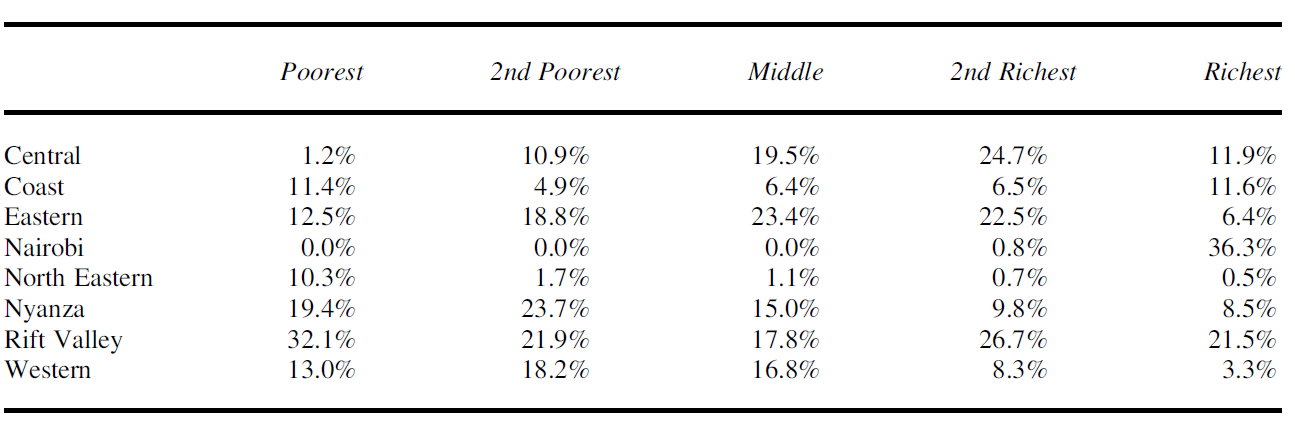
Measurement
Findings
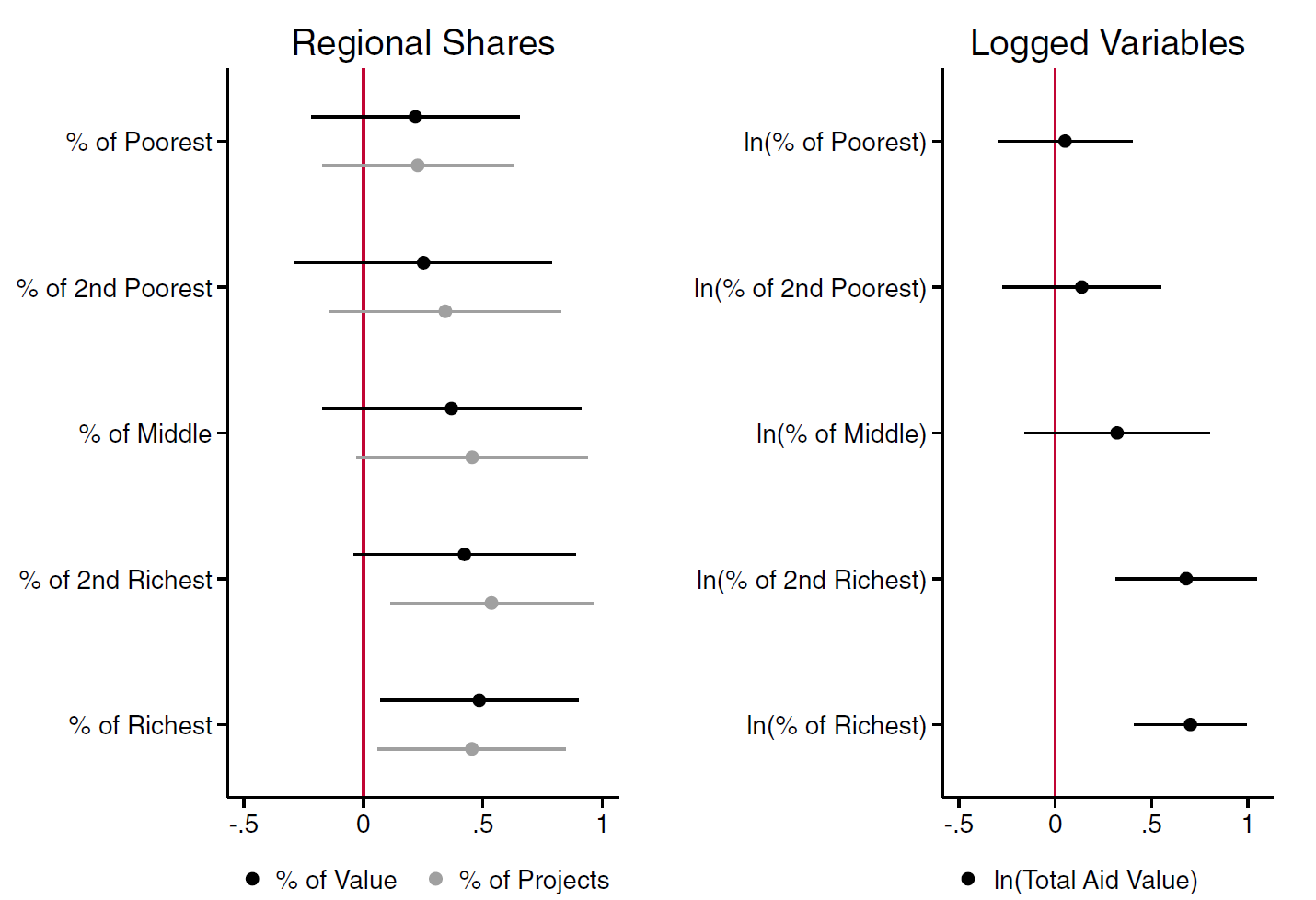
Findings
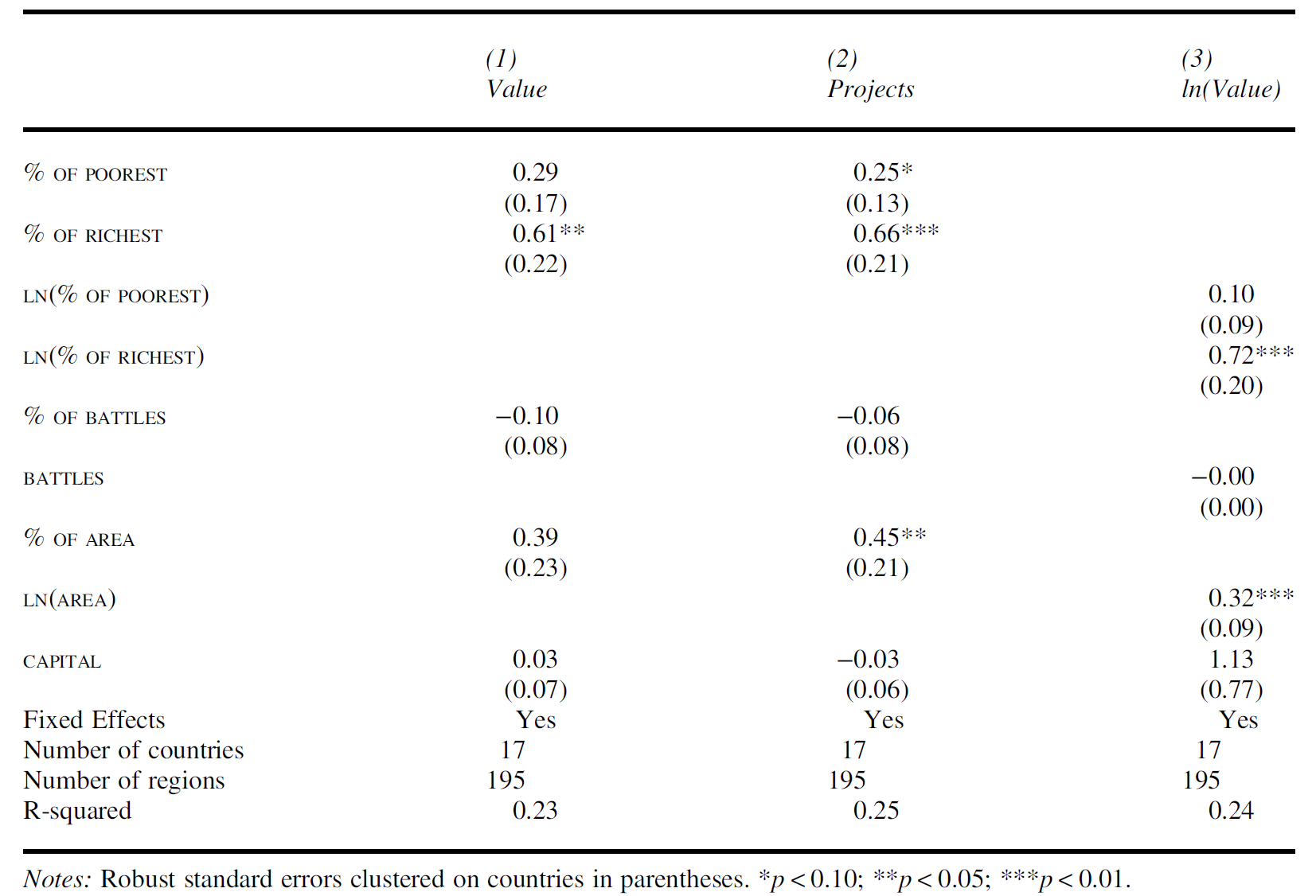
Policy Implications
- Majority of people live in middle-income countries, but is that where we should send aid?
Briggs (2021)
Research Design
Conjoint survey experiment
- Sample: World Bank Task Team Leaders
- Task: select projects based on important characteristics
- Outcomes: Client desirability, WB approval, implementation, impact
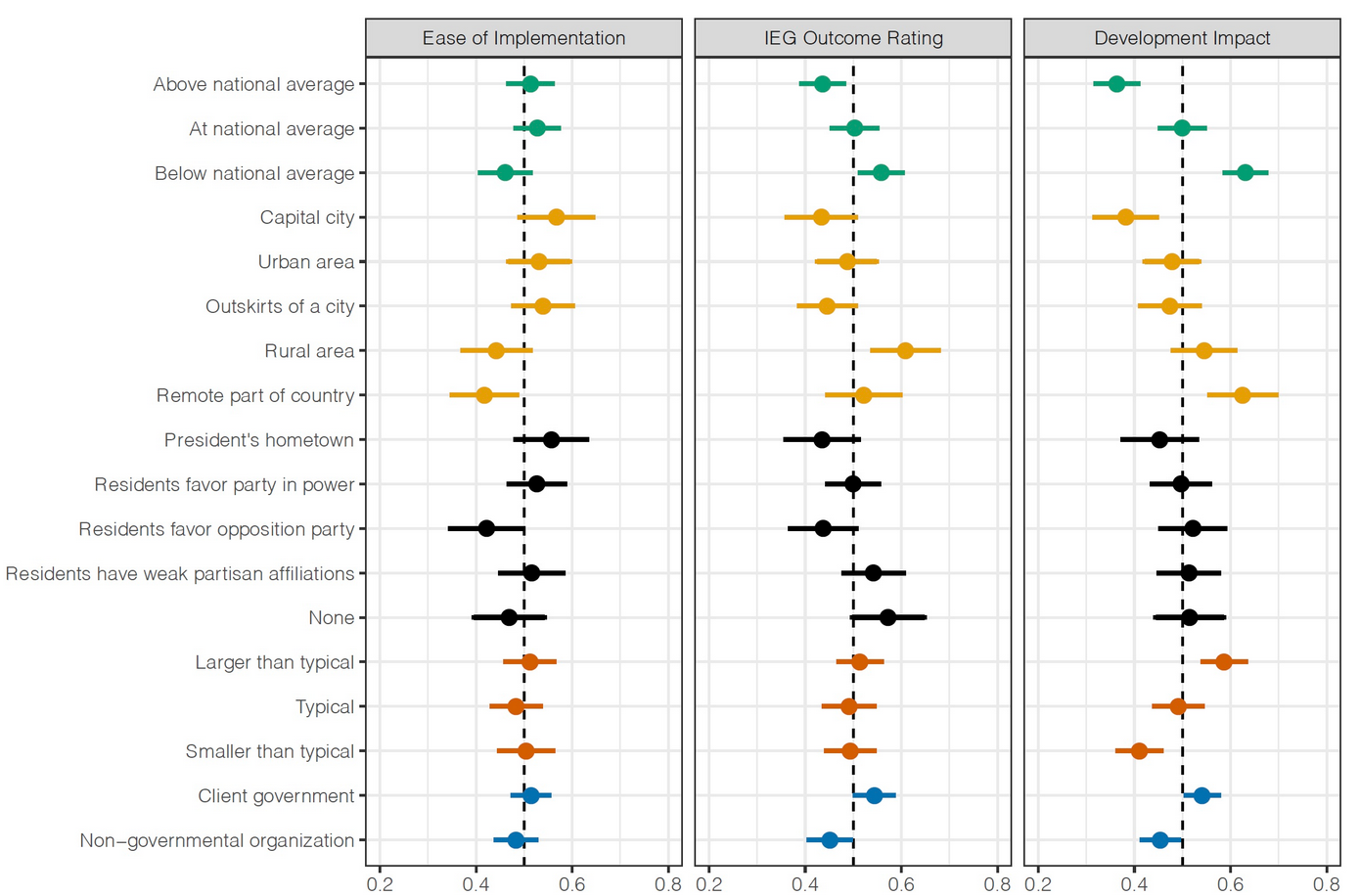
Research Question
What pressures shape the distribution of aid?
- Which projects the client government would prefer
- Which projects would be easier to get WB approval
- Which projects would be easier to implement
- Which projects would get better internal ratings
- Which project would be better for development
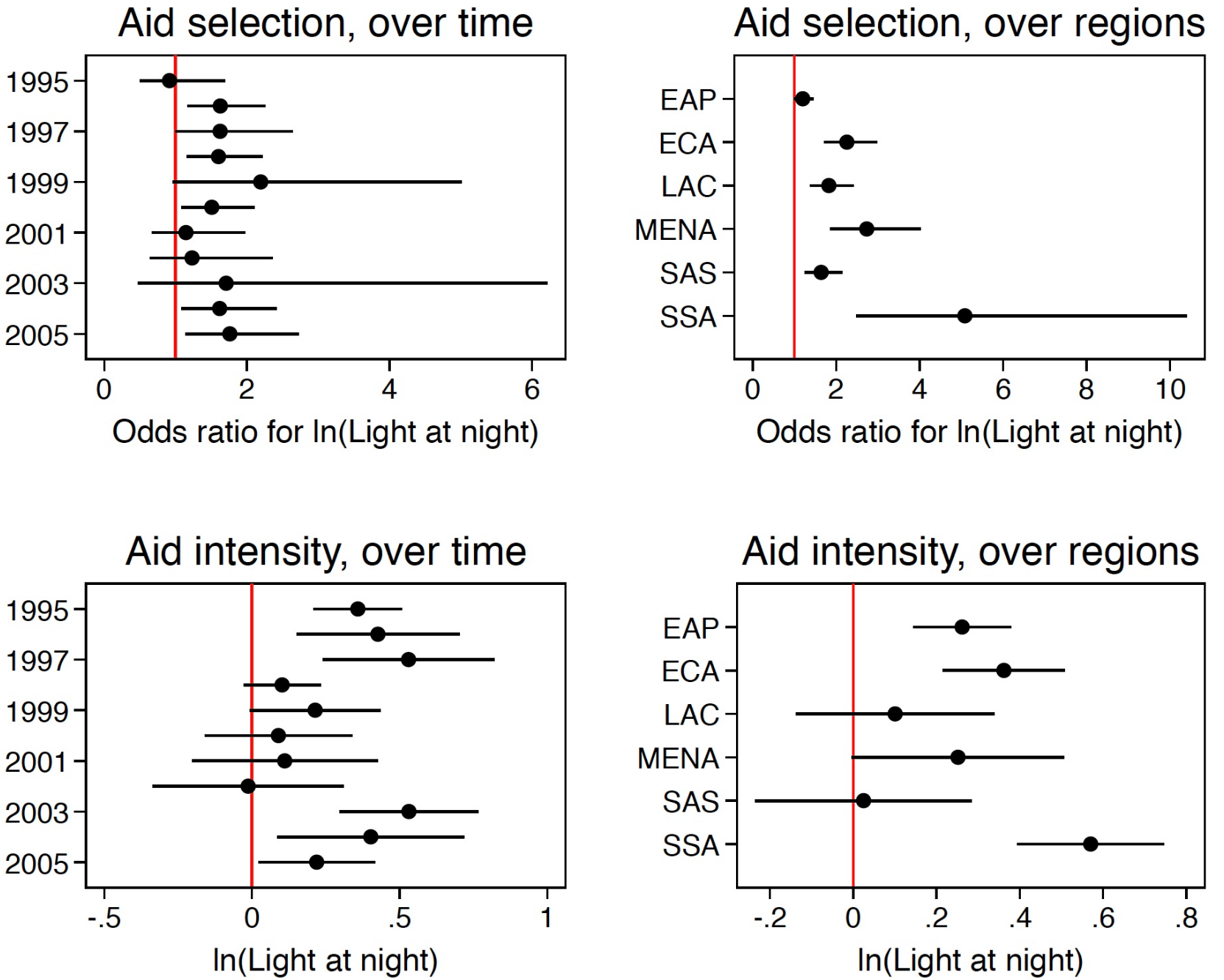
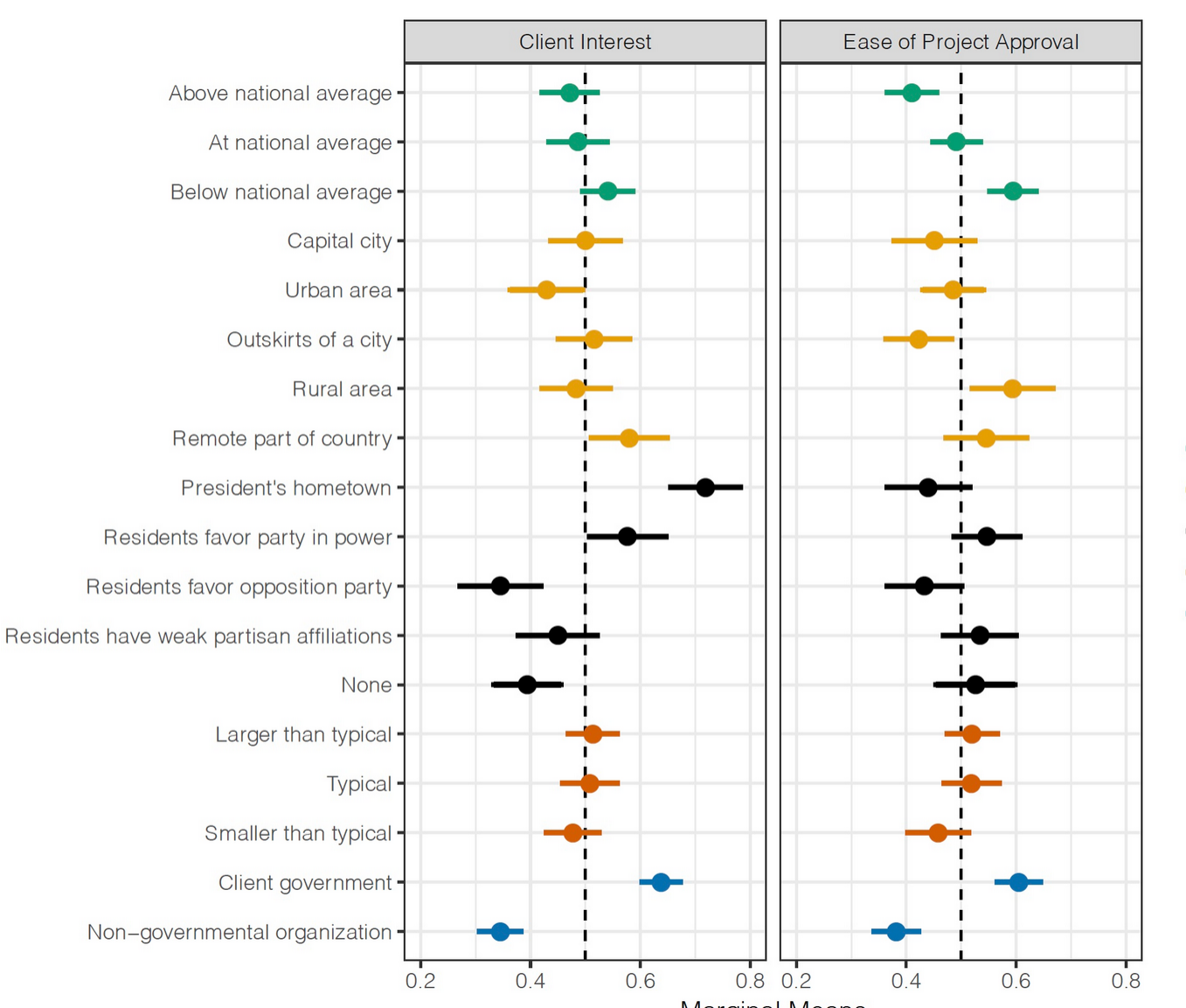
Findings
Findings
Findings
Client government desireability
- Positive: Hometown of the recipient country’s President
- Positive: Government implemented
- Neutral: Income of project location, urban
Ease of approval
- Positive: poorer places was easier to get approved
- Negative: presidential hometowns
- Negative: projects with smaller budgets
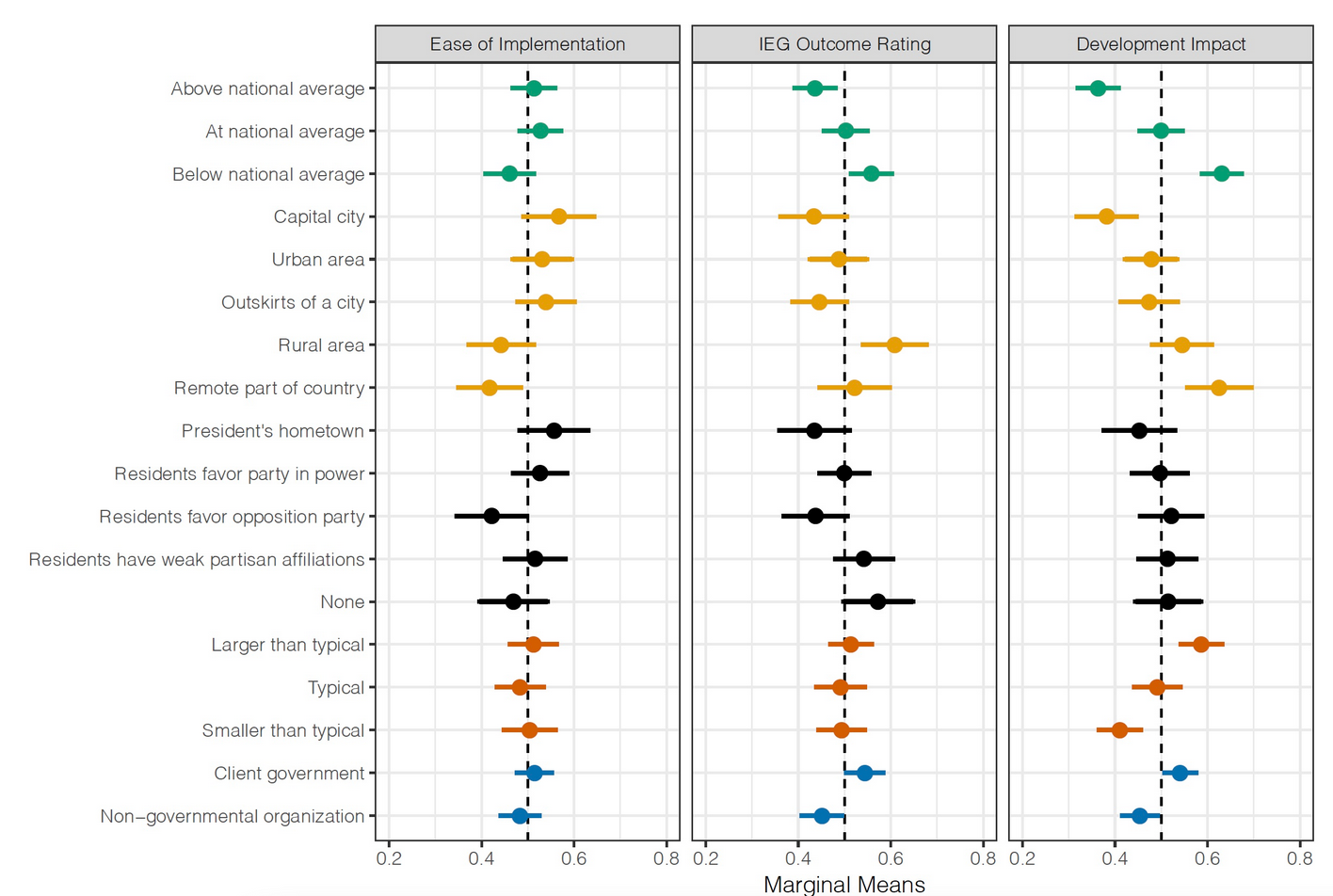
Findings
Development impact
- Positive: Poorer and rural areas
Ease of implementation
- Negative: Poorer and remote projects
- Getting more projects approved was either extremely or very important to their career
Findings
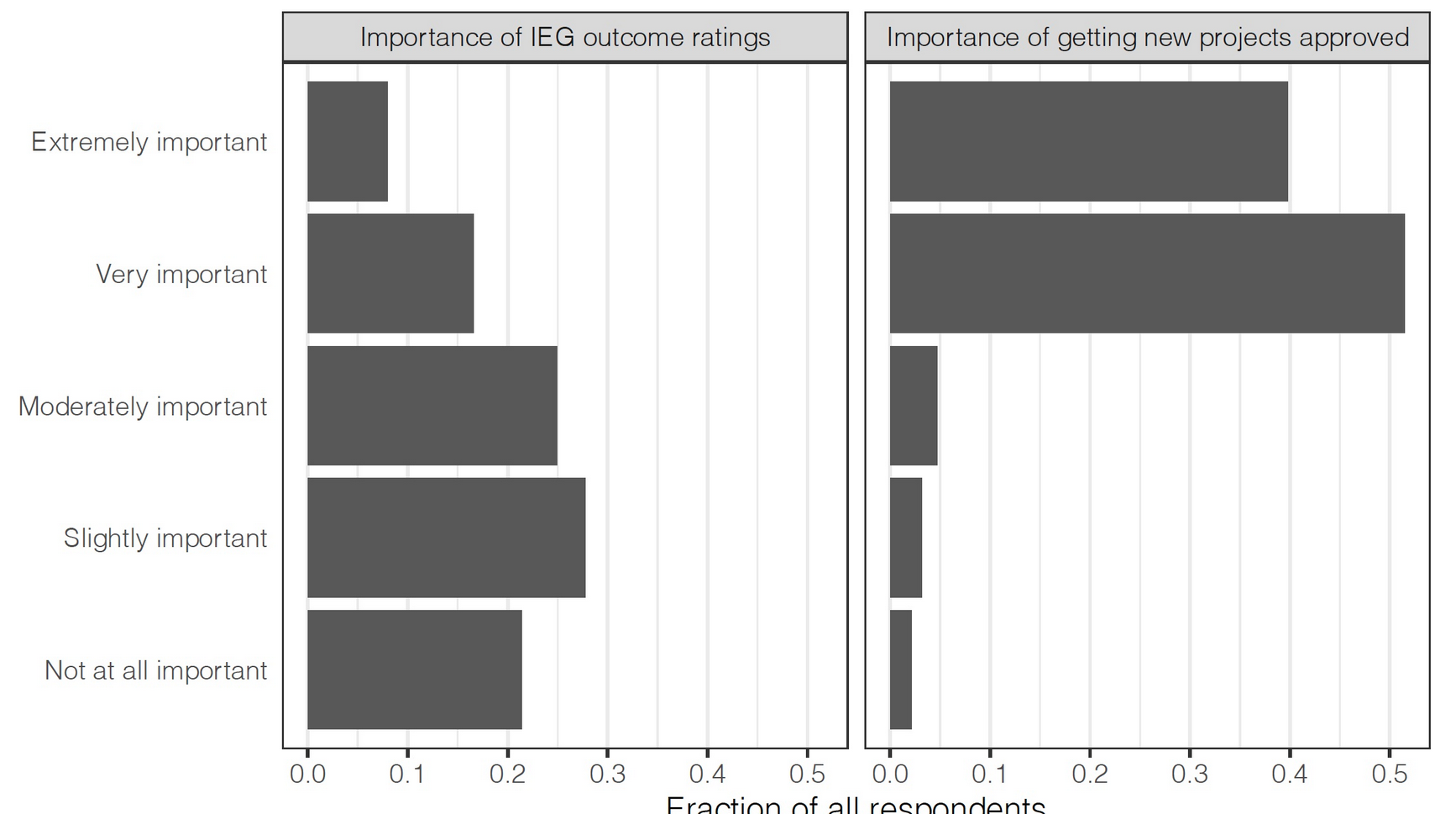
Findings
Findings
Findings